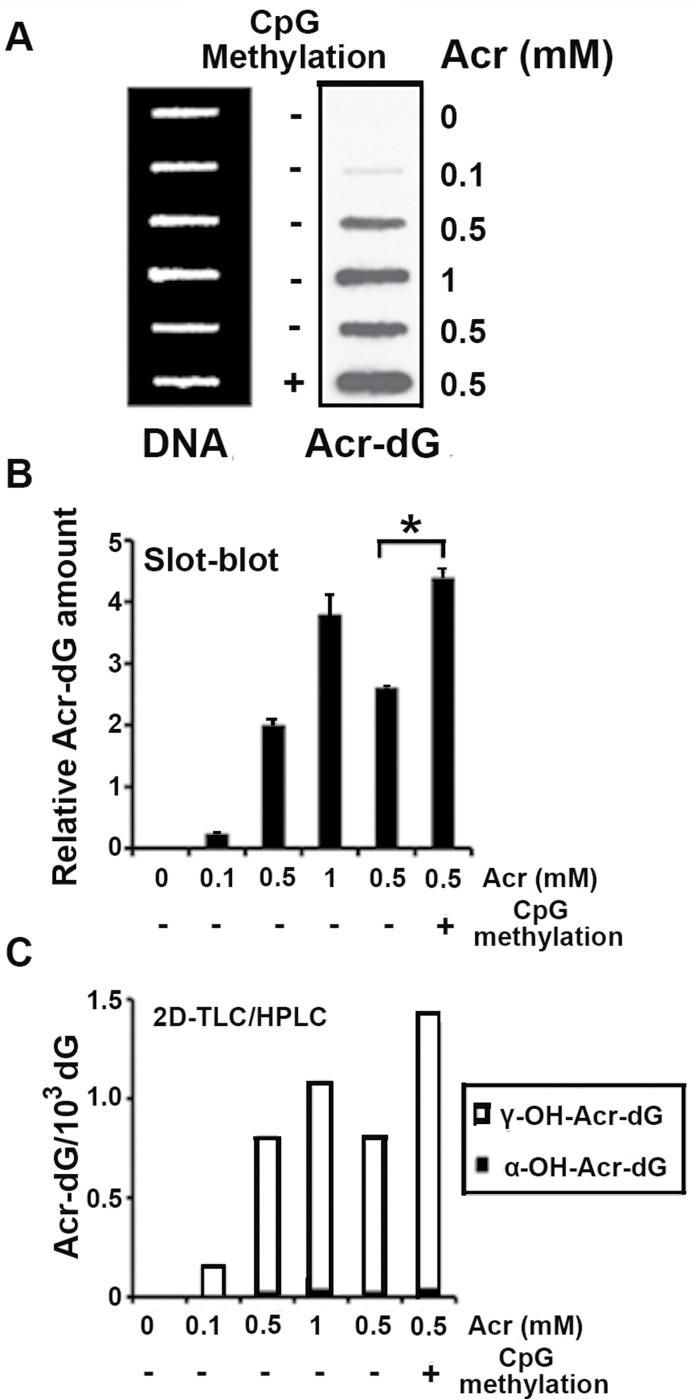
Fig. 1.
DNA methylation enhanced Acr-DNA adduct formation. Plasmid pSP189 DNA was methylated by the CpG methylase SssI, and the methylated and unmethylated pSP189 plasmids were modified with Acr (0–1mM). The amount of Acr-DNA adducts formed in the DNA was quantified by a slot-blot method with monoclonal Acr-dG antibody (A and B), and by the 32P postlabeling 2D TLC/HPLC method (C). (A) Acr-modified DNA (1 µg) was loaded onto nylon membrane using a slot-blot apparatus, the relative levels of Acr-dG adducts were detected using anti-Acr-dG antibody (right lane) and the relative amount of DNA on the same membrane was detected by methylene blue staining (left lane). (B) Quantifications of Acr-dG adducts from (A) using Acr-dG antibody signals, which were normalized by the amount of DNA. (C) Quantifications of the amount of Acr-dG formed in the pSP189 plasmid DNA by the 32P -postlabeling 2D TLC/HPLC method (* indicates P < 0.05).