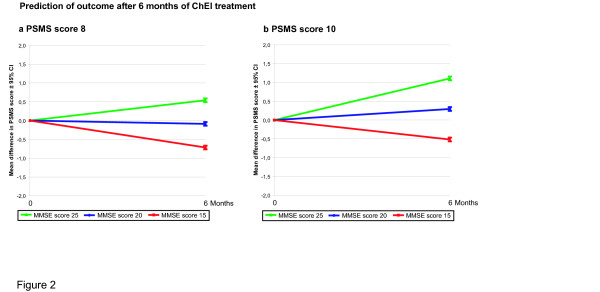
Figure 2.
Interaction effects between basic ADL and cognitive outcomes. Six-month mean Physical Self-Maintenance Scale (PSMS) outcomes with 95% confidence intervals predicted by the general linear models for patients with PSMS scores of: a. 8 and b. 10 at the start of ChEI treatment. A significant interaction effect was observed between cognitive and functional abilities at baseline (p = 0.008), i.e., a higher level of cognition and more impaired ADL ability implied increased response to ChEI therapy. In the figures, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores (15, 20 and 25 were chosen as arbitrary examples) were used to illustrate the interaction. The calculated outcomes were based on a 75-year-old patient who did not receive NSAID/acetylsalicylic acid treatment and had three medications at baseline.