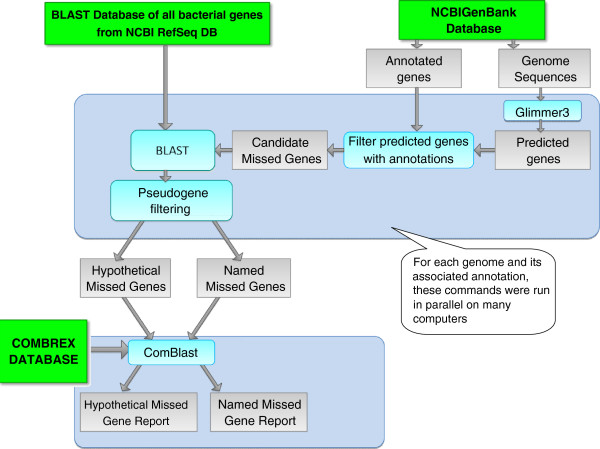
Figure 1.
Data flow through our analysis pipeline. Annotations and sequences were obtained from GenBank, and all sequences were processed with the Glimmer 3 gene finder to obtain gene predictions. Sets of predicted genes were filtered to exclude annotated genes and pseudogenes to obtain a set of candidate missed genes. These predicted genes were input as queries to BLAST against a database of all bacterial genes in RefSeq. Predicted genes were then designated as named missed genes or hypothetical missed genes, based on if they had a significant alignment to a non-hypothetical protein, or only aligned to hypothetical proteins, respectively. Each of these two sets were further analyzed by ComBlast, which uses BLAST and the COMBREX database to associate genes with additional attributes, such as experimentally determined function, 3D structure, conservation and phenotype information and assign a COMBREX support level to each potential missed gene.