Figure 3. Performance of the tempotron and other decoders on RGC population responses.
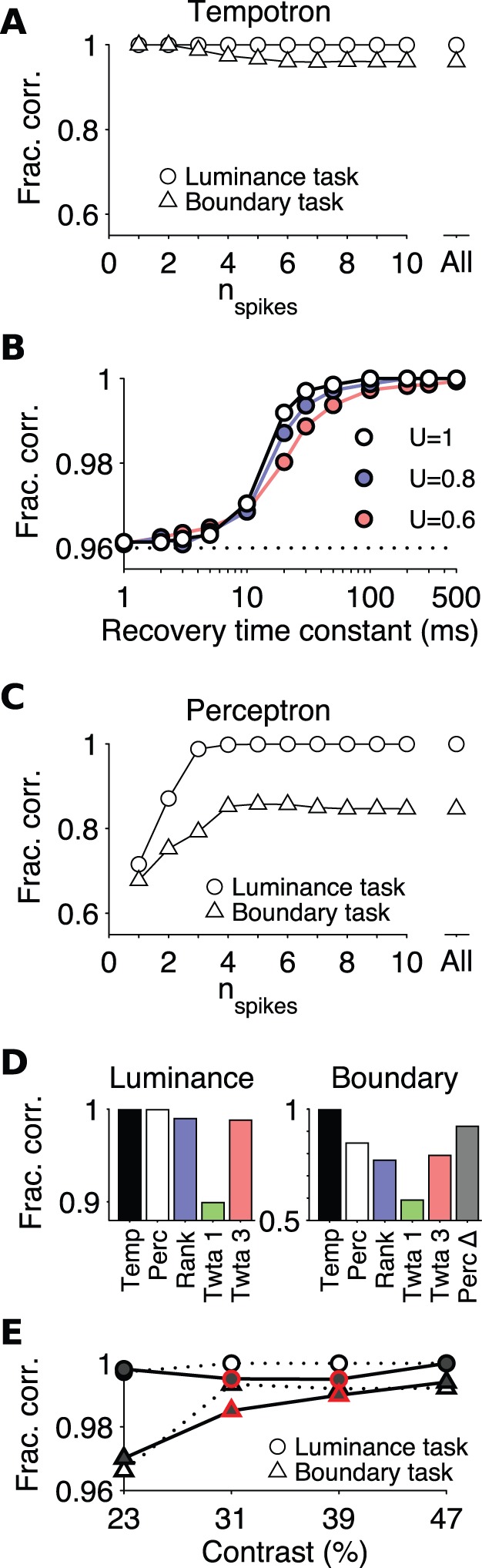
(A) Performance of the tempotron on the luminance (circles) and boundary (triangles) tasks in the highest contrast condition. Results are averaged over all realizations of each task and two separate populations of simultaneously recorded fast-Off RGCs, one with 7 neurons, the other with 8. The fraction of correct stimulus classifications is shown as a function of the maximal number of spikes admitted from each RGC. (B) Effect of synaptic depression on performance in the “all spikes” condition of the boundary task in (A). The fraction of correct responses is plotted as a function of the recovery time constant  of synaptic depression and the synaptic utilization parameter
of synaptic depression and the synaptic utilization parameter 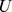 , which determines the degree of depression (cf. Equation 5);
, which determines the degree of depression (cf. Equation 5);  (maximal depression, black), 0.8 (blue), 0.6 (red). The dotted line indicates the performance with static synapses from (A). (C) As in (A), but performance of the perceptron decoder based on spike counts. (D) Comparison of the tempotron (Temp) and perceptron (Perc) peak performances from (A) and (C) with other timing-based readout schemes for the luminance (left) and boundary (right) tasks: Rank-order decoder (Rank), temporal-winner-take-all decoder using the first spike (Twta 1) or the first three spikes (Twta 3). The boundary task includes performance of a perceptron with an optimized integration window of 80 ms duration (Perc Δ). (E) Contrast dependence of tempotron performance in the luminance (circles) and boundary (triangles) tasks when using at most the first spike of each afferent ganglion cell. The fraction of correct classifications was measured separately within each of four contrast conditions (x-axis) on the basis of a seven-cell input population of RGCs. Open symbols with dotted lines: after training on all four contrast levels. Filled symbols with solid lines: after training only on the lowest and highest contrast levels. Note that the tempotron performs well even when generalizing to intermediate stimulus contrasts that were not encountered during training (colored symbols).
(maximal depression, black), 0.8 (blue), 0.6 (red). The dotted line indicates the performance with static synapses from (A). (C) As in (A), but performance of the perceptron decoder based on spike counts. (D) Comparison of the tempotron (Temp) and perceptron (Perc) peak performances from (A) and (C) with other timing-based readout schemes for the luminance (left) and boundary (right) tasks: Rank-order decoder (Rank), temporal-winner-take-all decoder using the first spike (Twta 1) or the first three spikes (Twta 3). The boundary task includes performance of a perceptron with an optimized integration window of 80 ms duration (Perc Δ). (E) Contrast dependence of tempotron performance in the luminance (circles) and boundary (triangles) tasks when using at most the first spike of each afferent ganglion cell. The fraction of correct classifications was measured separately within each of four contrast conditions (x-axis) on the basis of a seven-cell input population of RGCs. Open symbols with dotted lines: after training on all four contrast levels. Filled symbols with solid lines: after training only on the lowest and highest contrast levels. Note that the tempotron performs well even when generalizing to intermediate stimulus contrasts that were not encountered during training (colored symbols).
