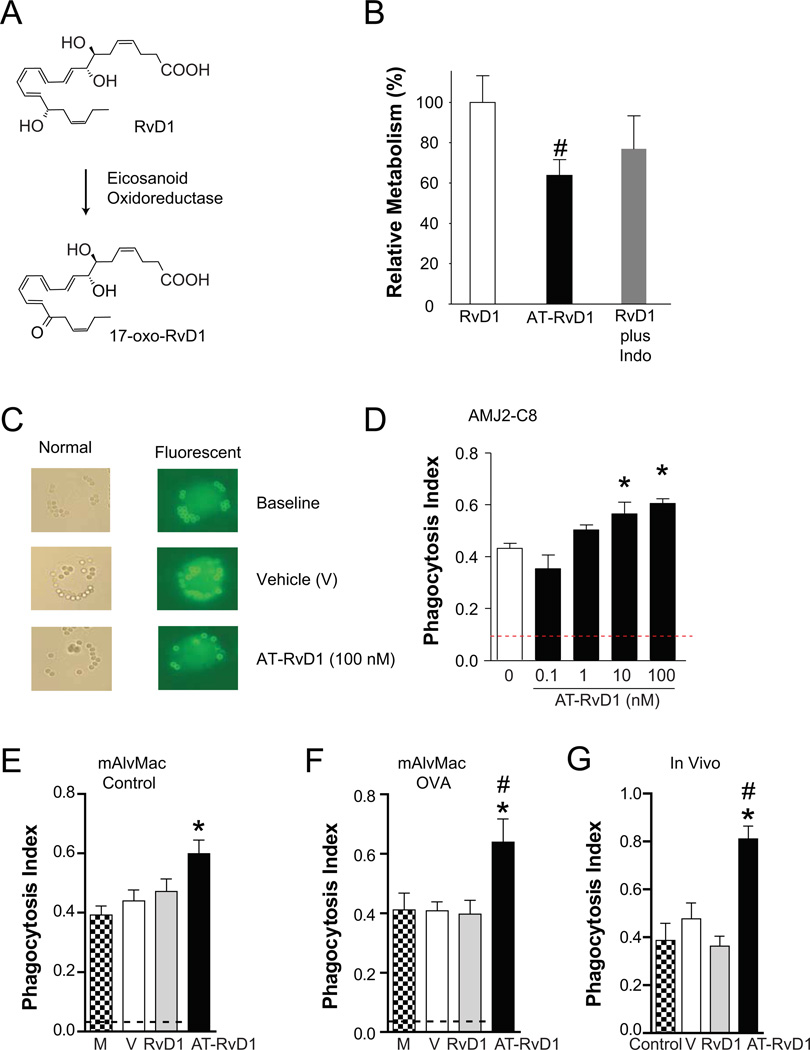
FIGURE 6.
AT-RvD1 resists metabolic inactivation by macrophages and stimulates macrophage clearance of allergen. Murine alveolar macrophages cells (AMJ2-C8) were incubated (30 minutes, 37°C) in the presence of RvD1 (in some cases with indomethacin) or AT-RvD1. Lipids were extracted and (A) RvD1 metabolites were identified and quantitated by LC-MS/MS analyses (see Methods). (B) Values are expressed as the relative percent 17-oxo-RvD1 metabolite relative to the total starting compound. (C) Macrophage phagocytosis of allergen was determined using rabbit anti-OVA IgG-coated beads (2 µm) that are detectable by light microscopy. In non-permeabilized cells, a fluorophore tagged antibody (FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody) was used to distinguish adherent (fluorescent) from internalized (non-fluorescent) beads. A phagocytosis index was calculated after 15 min in the presence of RvD1, AT-RvD1 (0.1, 10 and/or 100 nM), vehicle (V) or media alone (M) using (D) AMJ2-C8 cells in vitro or (E,F) alveolar macrophages (mAlvMacs) ex vivo that were isolated from BALF of (E) control or (F) OVA-sensitized and –challenged mice (Protocol day 21) (see Methods). The dashed black line indicates the baseline phagocytosis index. (G) The phagocystosis index was determined in vivo in OVA-sensitized or control mice 15 min after i.p. injection of OVA IgG-coated beads. In some animals, RvD1 (100 ng), AT-RvD1 (100 ng) or vehicle (0.1% ethanol) were given i.p. 5 min before introduction of the beads. Results represent the mean ± S.E.M. for two or more independent experiments. *P< 0.05 vs. vehicle, #P < 0.05 vs. RvD1.