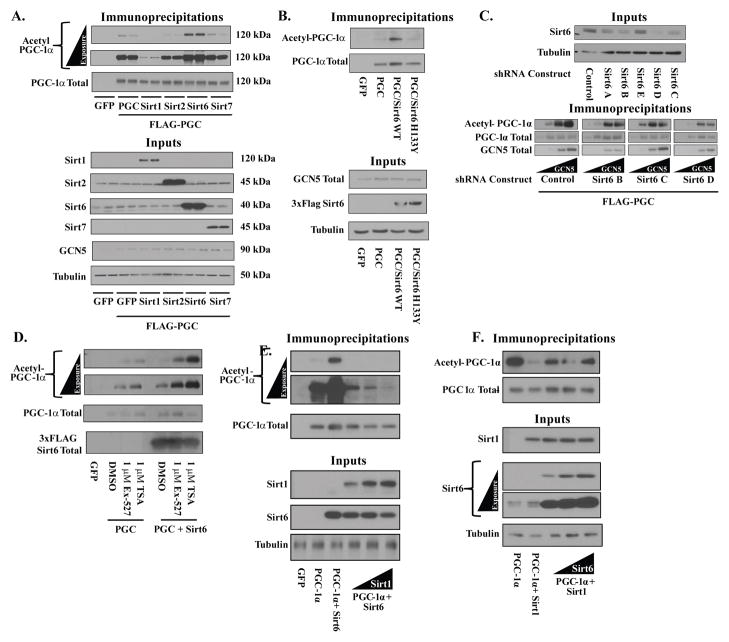
Figure 1. Sirt6 modulates PGC-1α acetylation in cultured cells.
(A) Effects of ectopic nuclear sirtuin expression on PGC-1α acetylation. FLAG-HA-PGC-1α was immunoprecipitated from U-2 OS cells transfected with Sirt1, Sirt2, Sirt6, Sirt7 or GFP control and blotted for total acetylation. Molecular weights of detected proteins are indicated. (B) Mutation of catalytically essential residue H133 blocks Sirt6-induced PGC-1α acetylation. (C) Knockdown of endogenous Sirt6 reduces PGC-1α acetylation levels. (Top) Sirt6 expression in U-2 OS lines stably expressing either one control shRNA or one of five different Sirt6 shRNAs (Bottom) PGC-1α acetylation from three of the lowest Sirt6 expressing lines co-transfected with PGC-1α and increasing amounts of GCN5. (D) 16 h inhibition of Sirt1 or Class I/II HDACs fails to block Sirt6-induced PGC-1α acetylation. (E) PGC-1α acetylation from U-2 OS cells transfected with a fixed concentration of Sirt6 and increasing amounts of Sirt1. (F) PGC-1α acetylation from U-2 OS cells transfected with a fixed amount of Sirt1 and increasing amounts of Sirt6. See Figure S1.