Figure 4. Neonatal hyperoxia exposure decreased CA1 and CA3 width but increased dentate gyral width of hippocampus in adult mice.
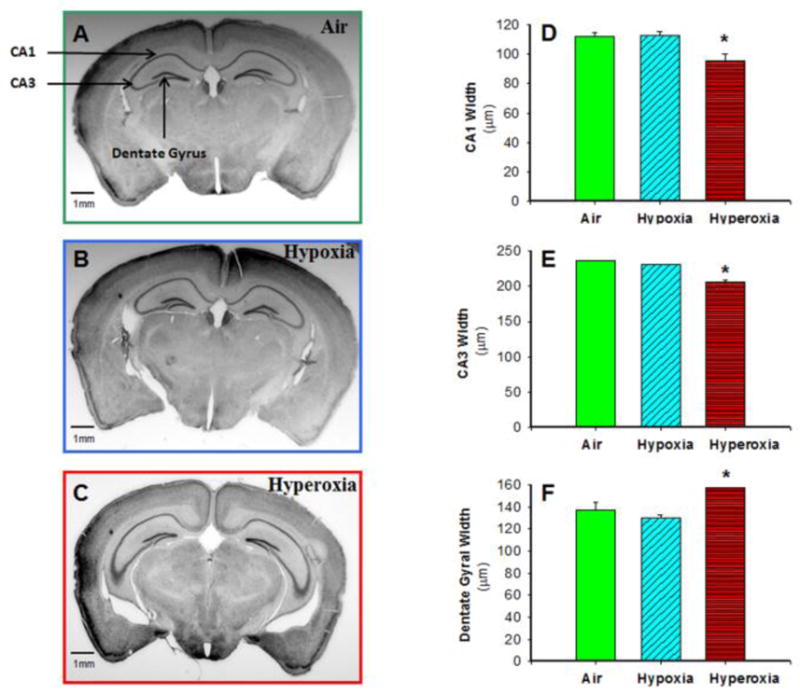
Photomicrographs of Nissl-stained adult mouse brain sections from air-exposed (A), hypoxia-exposed (B), and hyperoxia-exposed (C) mice were used to measure CA1, CA3, and dentate gyral width by image analysis. CA1 width (D) and CA3 width (E) in adult mice at approximately −2.1 mm bregma were lower, but dentate gyral width (F) was increased in adult mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia, as compared to mice exposed to air or hypoxia. Air-exposed: solid green bars, hypoxia-exposed mice: cyan angled stripes, hyperoxia-exposed: red bars with horizontal stripes; means± SEM; n= 11 in air, 7 in hypoxia, and 6 in hyperoxia.*p<0.05 vs. air-exposed mice. Calibration bar = 1 mm.
