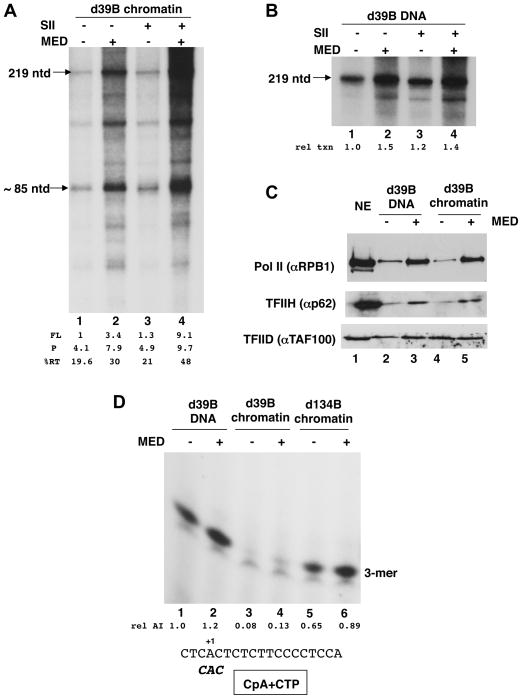
Fig. 4. Involvement of Mediator and SII at early steps in transcription of the d39B template.
A. In vitro transcription reactions using the chromatinized d39B template were done as in Fig. 2C, except that following PIC formation, transcription was allowed to proceed for only 12 min in the presence of radiolabeled NTPs. Mediator and SII were included as indicated. Other chromatin cofactors (PBAF, p300, FACT) were not added.
B. In vitro transcription reactions as in (A) except that the d39B was not chromatinized.
C. Immobilized template recruitment assay for selected PIC components. Scaled up transcription reactions were assembled on d39B templates (DNA, lanes 2,3; chromatin, lanes 4,5) as in (A). After PIC formation in the absence or presence of Mediator, templates were washed, and bound material was immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Chromatin cofactors (PBAF, p300, FACT, SII) were not included. Note that although pure factors were used in the binding assay, HeLa nuclear extract (NE, lane 1) served as immunoblot reference.
D. For abortive initiation reactions on the indicated templates, PICs were assembled (+/− Mediator) as for standard reactions (Fig. 2C) but reactions contained only the CpA dinucleotide primer, α32P-CTP and dATP. The trimeric product was visualized by autoradiography (25% PAG) and is marked (3-mer). The sequence around the Ad ML start site and the expected abortive product is shown.
See also Fig. S7.