Fig. 2.
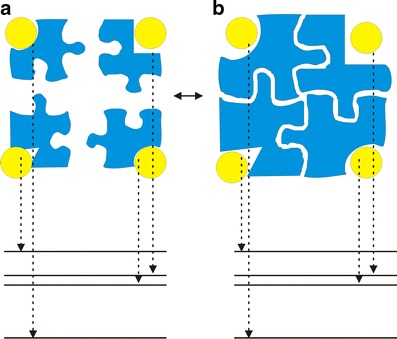
Illustration of the relationship between intrinsic specificity and conventional specificity as well as the corresponding energy spectrum. a The conventional definition of specificity is the difference(s) or discrimination(s) in affinity of the target receptor against other receptors binding to the same ligand; b the definition of intrinsic specificity is the difference(s) or discrimination(s) in binding energies of native (lowest) binding mode or site against other non-native binding modes (pockets) for a ligand binding to a receptor. The giant receptor here can be considered as the combination of many smaller receptors connected by certain linkers. When the giant receptor is large enough to cover all the possible ligand–protein interactions, the definition of intrinsic specificity is equivalent to the definition of conventional specificity. The receptors are colored blue; the yellow ball represents the ligand
