Table I.
In silico, In vitro, and In vivo Data to Predict the BCS/BDDCS Class of Seven Novartis Compounds
| Parameter | NVS732 | NVS406 | NVS562 | NVS701 | NVS001 | NVS169 | NVS113 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In silico preliminary BCS/BDDCS | |||||||
| Calculated log P, or LogDpH = 7.4 | 0.83 | 3.4 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 1.0 (log DpH = 7.4) | 5.0 | 4.6 |
| Calc. human perm., P eff (10−4 cm/s)a | 0.56 (low) | 2.47 (high) | 3.13 (high) | 1.34 (low) | 1.63 (low) | 0.21 (low) | 1.24 (low) |
| Calc. intrinsic solubility (mg/mL)b | 14.1 (high) | 0.0026 (low) | 0.0036 (low) | 0.0028 (low) | 6.77 (high) | 0.077 (low) | 0.11 (low) |
| Probability of extensive metabolism | Low | High | High | High | Low | High | High |
| pBCS/pBDDCS class | 3/3 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 4/2 | 3/3 | 4/2 | 4/2 |
| Rat BDDCS (ADME study with radiolabeled compounds) | |||||||
| Rat dose numberc | 2.8 | 1286 | 3214 | 857 | 0.007 | 6.59 | 51.4 |
| F a (%)d | 87 | 45 | >80 | 26–34 | 8.5 | 29 | 27 |
| Elimination pathway in Rat (% of dose recovered after an i.v. administration) | |||||||
| Urinary excretion of intact drug | 26.9 | 0.1 | 0.5e | 0.0 | 5.0 | 2.54 | < 0.1 |
| Biliary excretion + GI secretion | 8.6 | 9.7 | 99.5e | 15.3 | 77.7 | 15.4 | 35 |
| Percent metabolism | 64.3 | 90.2 | N/A | 84.7 | 17.3 | 81.3 | 65 |
| rBCS/rBDDCS class | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Human BCS/BDDCS | |||||||
| Dose number for drug substances (DS)f | 0.013 | 600 | 1500 | 400 | 0.003 | 3.07, 0.51 (ME) | 24, 1.7 (SF) |
| F or F a (%), fasted condition | F: 85 | F: 20 (susp.) | F a: 50–97 (G + pred.) | F a < 30 (G + pred.) | F: ∼3.0 | F a >90 (ME) Simcyp pred. | F a > 92 (SF) G + pred. |
| Transporter effects | Weak P-gp substrate | P-gp substrate | Minimal P-gp effects | Weak P-gp substrate | Substrate for uptake transporters | P-gp substrate | Weak P-gp substrate |
| Pred. hBCS/BDDCS Classg | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Pred. human food effects | No | Positive | Positive | Positive | Negative | No | No |
| Obs. human food effectsh | No | Positive | Positive | Positive | Negative | No | Negative |
| Obs. hBCS/hBDDCS Classg | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2i | 4j |
aHuman effective permeability was calculated by GastroPlus ADMET predictor. Metoprolol was used as a high permeability marker, thus calculated P eff > 1.8 × 10−4 cm/s indicate high permeability
bLowest water solubility (milligrams per milliliter) over the pH range 1–8 calculated by GastroPlus ADMET predictors. A value > 0.5 mg/mL was defined as high solubility
cDose number (rat) = human equivalent dose (milligrams per kilogram)/water solubility of drug substance (milligrams per milliliter)/maximum dose volume (10 mL/kg). The equivalent dose in rats is approximately 6 fold of the highest human dose tested in clinical food effects study
dFraction absorbed calculated based on the following equation (41). If non-radiolabeled compounds are used, F
a can be estimated by equation of “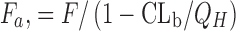 ”, where Q
H (hepatic blood flow) = 3.3 L/h/kg and CLb is the blood clearance
”, where Q
H (hepatic blood flow) = 3.3 L/h/kg and CLb is the blood clearance
eCompound related radioactivity recovered
fDose number (human) = dose (milligrams)/water solubility of drug substance or formulation (milligrams per milliliter)/maximum dose volume (250 mL). Water solubility of each compound is listed in Table II
gThe hBCS/BDDCS class is predicted based on estimated or observed human bioavailability for clinical service dosage form. The category of human BDDCS class for a compound can be formulation and dose dependent. The hBCS/BDDCS of a drug product is finalized or confirmed by the direction of observed human food effects
hThe observed magnitudes for clinical food effects for each compound were listed in Table III
iLack of food effect demonstrates potential class 1 behavior, due to low dose and optimized formulation
jNegative food effect may be the result of optimized solubility in fasted state
DS drug substance, ME microemulsion, SF solid formulation
