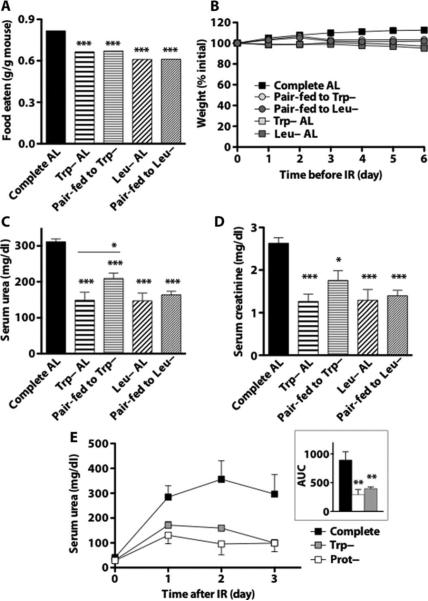
Fig. 2.
Protection against renal IR by isolated EAA deprivation. (A) Total food intake over 6-day preoperative period expressed as weight of food eaten per total weight of animals in the cage (n = 2 cages per group). (B) Body weights of mice fed complete, Trp– or Leu– chow ad libitum (AL) or pair-fed (PF) to Trp– or Leu– animals with complete chow over the 6-day preoperative period (n = 8 per group) expressed as percent initial weight. (C and D) Kidney function as measured by serum urea (C) and creatinine (D) 1 day after 25 min of renal IR. (E) Effect of isocaloric protein- (Prot–) and tryptophan-deficient diets on kidney function, as measured by serum urea. Mice were preconditioned for 1 week on the indicated diet restricted daily to 0.28 kcal per gram of initial weight (~35% DR) before and up to 3 days after 30 min of renal ischemia (n = 5 per group). Inset: Area under the curve (AUC) analysis. Error bars indicate SEM. Asterisks indicate the significance of the difference between the indicated group and the complete diet group according to a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test, or between the Trp– or Leu– groups and their respective pair-fed controls as indicated with Bonferroni'smultiple comparison test. *P <0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.