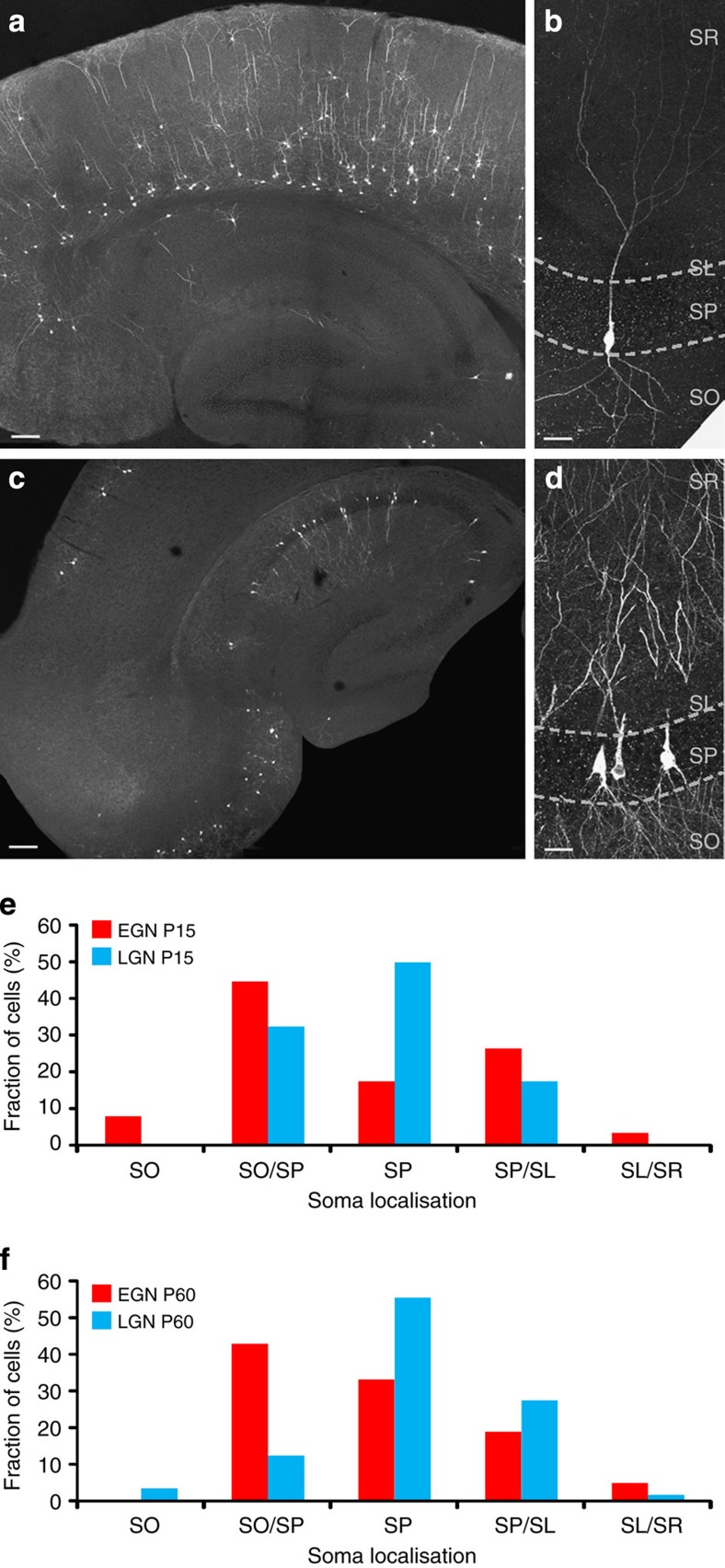
Figure 5. The spatial distribution and morphological features of hippocampal EGNs/LGNs are similar at juvenile and adult stages.
Fate-mapped neurons are visible in the hippocampus and neocortex after GFP immunofluorescence detection in Ngn2CreERTM;RCE:LoxP mouse slices at P15. As at P60 (Fig. 4), EGNs are relatively sparse in the hippocampus (a,b, tamoxifen gavage at E12) in comparison with LGNs (c,d, tamoxifen gavage at E15) throughout the CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus. Early-generated pyramidal cells are preferentially localized in the deeper part of the stratum pyramidale (sp) of CA3a/b (a), while LGNs are distributed throughout the radial width of the stratum pyramidale (d). Note that EGNs populate the deeper layers of the neocortex (Cx) while LGNs are present in superficial layers. so: stratum oriens, sr: stratum radiatum, sl: stratum lucidum. Scale bars: 150 μm in a,c; 37.5 μm in b,d. (e,f) Spatial distribution of the somata of EGNs (red, tamoxifen gavage at E12) and LGNs (blue, tamoxifen gavage at E15) along the radial axis of the CA3 hippocampal region measured at P15 (e) and P60 (f). Note that similar distributions are obtained at P15 and P60, with EGNs preferentially located at the border between stratum pyramidale and stratum oriens (SO/SP) and LGNs located within the stratum pyramidale (SP). SO, stratum oriens, SO/SP, border between stratum pyramidale and stratum oriens, SP, stratum pyramidale, SP/SL, border between stratum pyramidale and stratum lucidum, SL/SR, border between stratum lucidum and stratum radiatum.