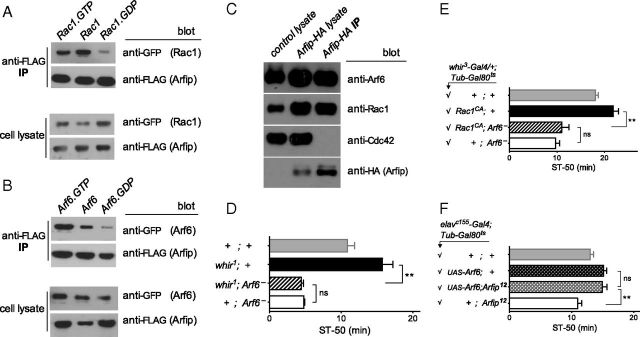
Figure 7.
Arfaptin binds to activated GTPases and transduces a signal from Rac1 to Arf6. A, Arfip preferentially binds to the GTP-locked forms of Rac1 and Arf6 in B. Drosophila S2 cells, stably expressing Arfip–FLAG, were transiently transfected with Rac1–YFP or Arf6–YFP. GTPases pulled down with anti-FLAG beads were then detected with anti-GFP antibody, and representative pull-downs of multiple independent ones are shown. Mutants used were Rac1G12V (GTP-locked), Rac1T19N (GDP-locked), Arf6Q67L (GTP-locked), and Arf6T44N (GDP-locked). C, Arfip–HA interacts with Rac1 and Arf6 but not Cdc42 GTPase in vivo. Western blots of control lysate, Arfip–HA lysate (expressing UAS–Arfip–HA in the nervous system with elavc155–Gal4), and Arfip-HA pulled down with anti-HA were probed with anti-GTPase or anti-HA antibody. The lysate lanes represent 5% of the immunoprecipitation (IP) pull-down input. D, E, Double mutants of ethanol-sensitive Arf6− with ethanol-resistant whir1 (in D) or activated Rac1 (in E, UAS–Rac1CA, driven with whir3--Gal4/+ in the adult only as in Fig. 5B using Tub–Gal80ts to avoid developmental lethality) are no different from ethanol-sensitive Arf6− mutants alone, indicating that Arf6 acts downstream of RhoGAP18B and Rac1 (NS, p = 0.25, **p < 0.001, n > 7 per genotype for D; NS, p = 0.44, **p < 0.001, n > 6 per genotype for E). Arf6− is Arf6KG/P2 for both panels. F, The ethanol-resistant UAS–Arf6 overexpression phenotype is unchanged when ethanol-sensitive Arfip12 is introduced, indicating that Arf6 acts downstream of Arfip (NS, p = 0.85, **p < 0.001, n > 6 per genotype; pan-neuronal elavc155–Gal4/+ was used to drive UAS–Arf6 in the adult only as in Fig. 5C).