Figure 3.
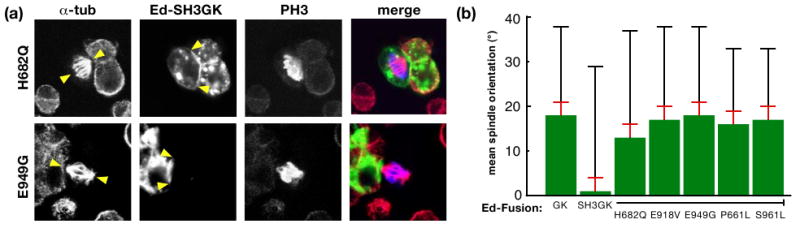
The SH3 domain regulates GK domain function. (a) Example cells from spindle orientation assay. Mitotic S2 cells were stained with antibodies against α-tubulin (red) to identify the mitotic spindle, the FLAG tag (green) to identify Ed-SH3GK with either H682Q or E949G point mutations, and Phospho-Histone H3 (blue) to identify DNA. Arrows denote spindle position (in α-tubulin channel) or edges of Ed-fusion crescent (in Ed channel). Merged images show mitotic spindle alignment to fusion protein crescents. (b) Spindle orienting ability of Ed-Dlg fusions. The mean spindle orientation angle is shown for Ed fusions to Dlg-GK or Dlg-SH3GK (wild type and those harboring putative activating mutations). The mean spindle orientation angle is the difference between the random angle (45°) and the mean observed angle for a particular Ed fusion. The standard error (calculated by measuring the mean angle from several independent experiments; see methods) is shown as an orange bar whereas the standard deviation (due to the natural variation of the population of cells) is shown as a black bar.
