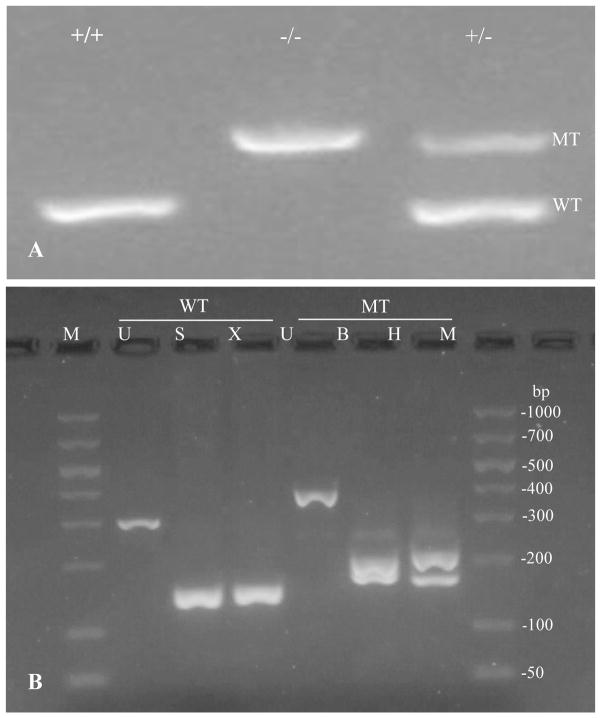
Figure 1.
Genotype verification in litter mates by PCR amplification of tail genomic DNA. (A) Specific wild type allele primers generated a 294bp fragment in the homozygote wild type (oxgr1+/+) and heterozygotes (oxgr1+/−) animals. Specific mutant allele primers amplified a 378bp fragment of the selection cassette that generated homozygotes null (oxgr1−/−) via homologous recombination. (B) Restriction analysis of the amplified fragments from wild type and mutant alleles. The amplified wild type fragment yielded a 152 and 142bp in SmaI digestion, and a 150 and 144bp in XmaI digestion. The amplified mutant allele subjected to BamHI digestion resulted in 177 and 201bp, while HindIII reduced the fragment to 168 and 210bp. M; 50–1000bp DNA ladder, U; uncut, S; SmaI, X; XmaI, B; BamHI, and H; HindIII.