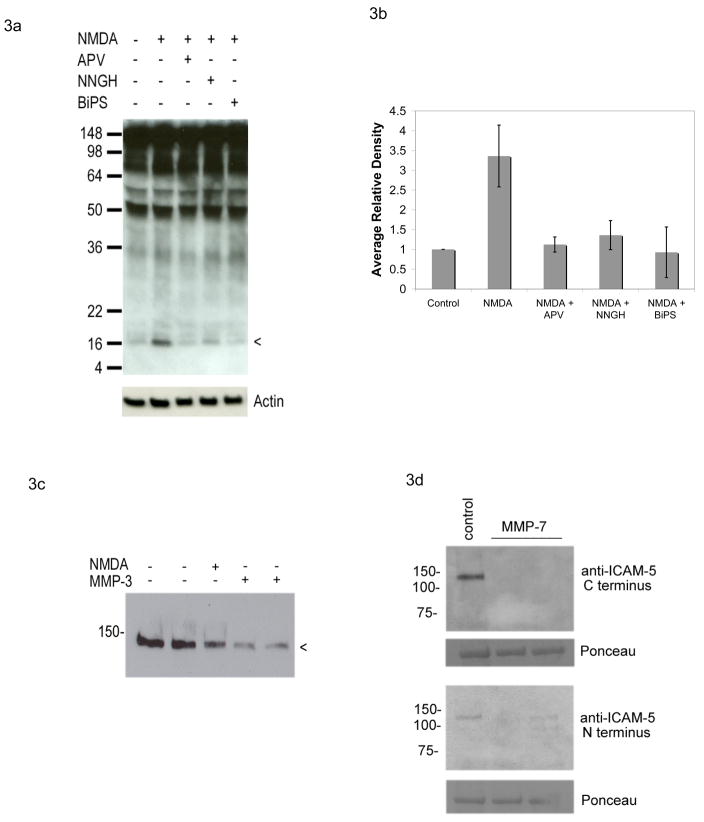
Figure 3. MMPs mediate rapid NMDA dependent shedding of ICAM-5.
Dissociated neuronal cultures were stimulated for 15 minutes with 100 μM NMDA, in the presence or absence of the NMDA receptor blocker APV or the MMP activity inhibitors NNGH or BiPS as indicated. Lysates were then prepared and analyzed by Western blot with an antibody to the C terminal domain of ICAM-5. As shown in Figure 3a, which is representative of 3 experiments, NMDA was again associated with generation of the 16 kDa CTF of ICAM-5 and this was inhibited by pretreatment of cells with 50 mM APV as well as by either 3.2 μM NNGH or 25 μM BiPS. Figure 3b represents densitometric analysis of results, for which differences between control and NMDA were significant (P< 0.05) while differences between control and other treatment groups were not. For figure 3c, neurons were stimulated for 30 minutes with 100 μM NMDA or 100 ng/ml MMP-3, as indicated, and lysates analyzed by Western blot with an antibody to the exodomain. A reduction in immunoreactivity can be appreciated with both NMDA and MMP-3. For figure 3d, neurons were stimulated for 30 minutes with 100 ng/ml MMP-7, as indicated, and lysates analyzed by Western blot with N or C terminal specific antibodies as noted. The major band at approximately 50 kDa seen with Ponceau staining is shown as a loading control. A reduction in ICAM-5 immunoreactivity can be appreciated with MMP-7.