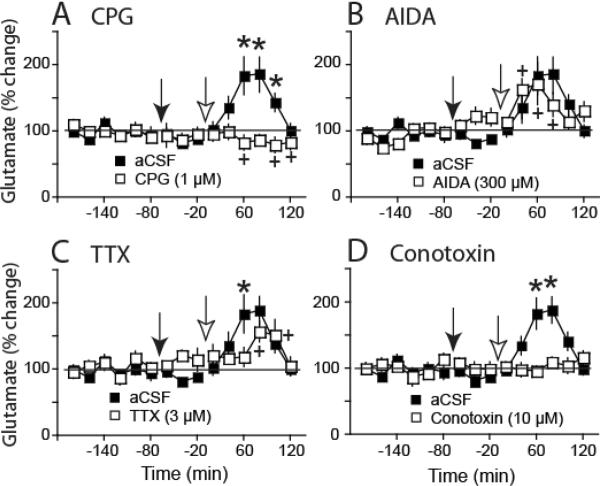
Figure 3.
Modafinil increases in glutamate were abolished by CPG and conotoxin, and were partly antagonized by TTX. A) CPG (1μM, filled arrow; a cystine-glutamate exchange inhibitor) was introduced into the dialysis buffer 60 min prior to injecting modafinil (open arrow) and prevented the rise in glutamate, indicating dependence of this effect on cysteine-glutamate exchange. B) AIDA (300 μM; a mGluR1 antagonist) was without effect on modafinil-induced glutamate. C) TTX (3 μM; a voltage-dependent sodium channel inhibitor) produced a partial reduction in modafinil-induced glutamate, indicating partial mediation of this effect by impulse-dependent glutamate release. D) Conotoxin [10 μM; a voltage gated calcium channel (Cav) inhibitor] prevented modafinil-mediated increases in glutamate, suggesting dependence of this effect upon Cav. The aCSF group is repeated in each panel. *p <0.05 compared to aCSF group, + p< 0.05 compared to baseline within group.