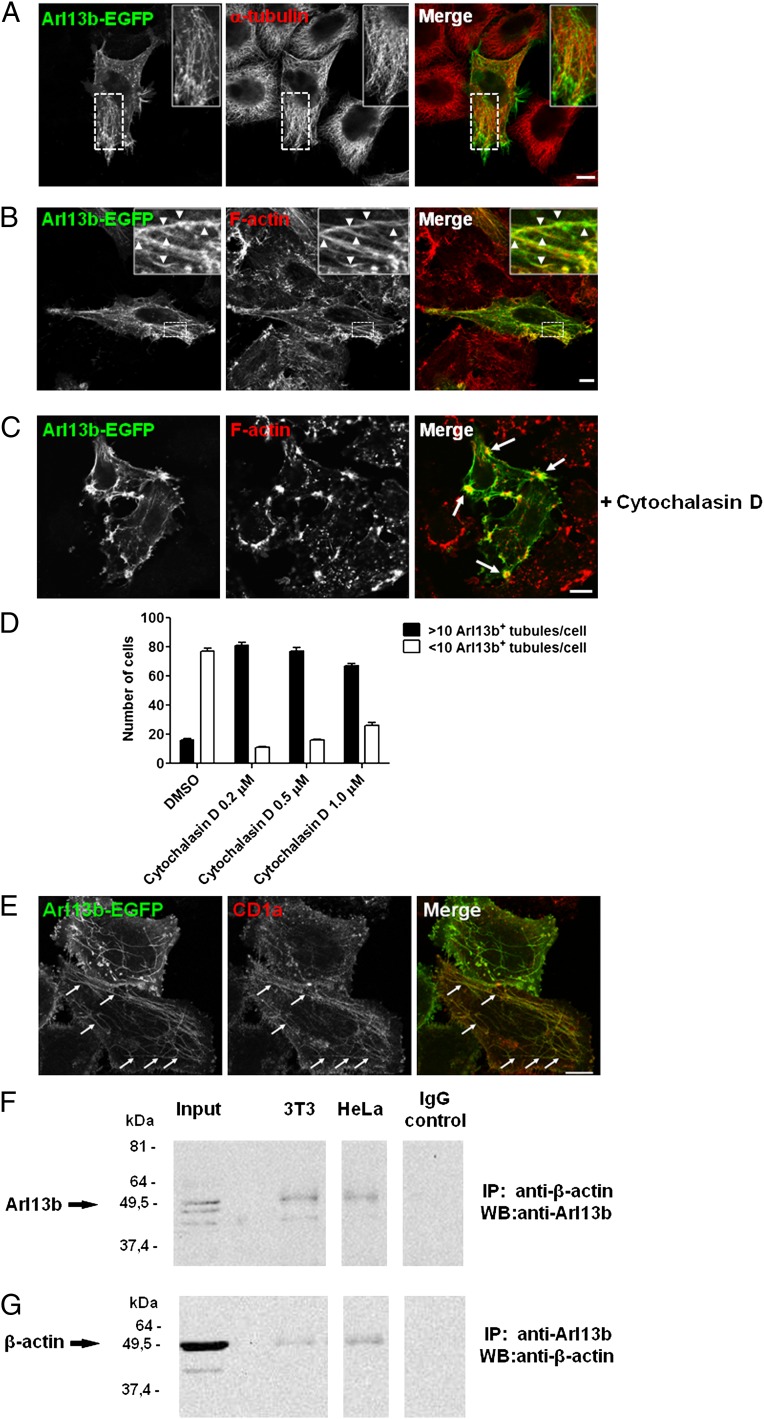
Fig. 4.
Arl13b interacts with actin. (A–C) HeLa cells were transfected with Arl13b-EGFP for 24 h, treated with 5 µM of cytochalasin D for 45 min (C) or untreated, fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti–α-tubulin Ab (A) or Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated phalloidin, which labels filamentous actin (B and C) (red). Arrowheads indicate actin filaments that colocalize with Arl13b tubules. Arrows indicate plasma membrane accumulations of actin and Arl13b. (D and E) HeLa:CD1a stable transfectant cells were transiently transfected with Arl13b-EGFP for 24 h, treated with cytochalasin D for 45 min at the indicated concentrations (0.2 µM in E), fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-CD1a mAb (red). The number of Arl13b tubules per cell was counted (n = 95) and grouped into cells with >10 and <10 tubules per cell (D). Arrows indicate Arl13b and CD1a colocalization in tubules (E). Results are representative of two independent experiments. (F and G) HeLa and NIH 3T3 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with mouse monoclonal anti–β-actin (F) or rabbit polyclonal anti-Arl13b (G) Ab, separated by SDS/PAGE, and immunoblotted with anti-Arl13b (F) or anti–β-actin (G) Ab, followed by HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary Ab, respectively. Rabbit and mouse IgG were used as negative controls. (Scale bars: 10 μm.)