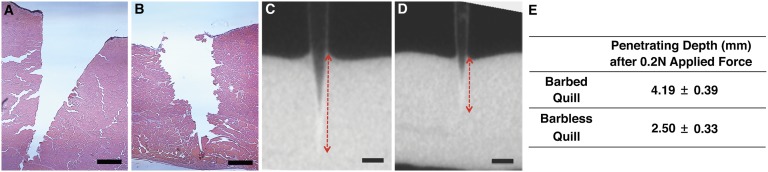
Fig. 2.
Barbs reduce tissue damage and facilitate penetration into tissue. (A, B) Representative histological images of tissue samples that were penetrated with barbed and barbless quills, respectively, showing significantly less damage induced by the barbed quills (n = 5). (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (C and D) Microcomputed tomography (Micro-CT) images present the penetrated barbed (C) and barbless (D) quills within tissue. Both quills were penetrated into tissue with an applied force of 0.2 N. The red dashed arrows indicate the penetrating depth of quill. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) (E) Mean penetrating depth of barbed and barbless quills observed in micro-CT images (n = 3).