Fig. 6. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays of fragments containing the CepR2 binding site.
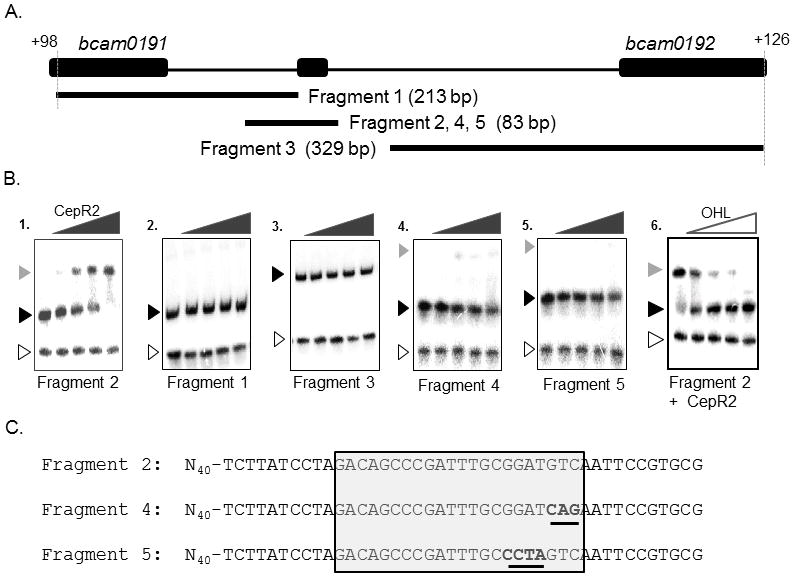
A: location and size of DNA fragments used in Part B. B. Clarified supernatants containing CepR2 were used for all binding reactions. A 65-bp PCR amplified lacZ DNA fragment was used as a negative control (open arrowhead). Free DNA is indicated using a black arrowhead, while CepR2-DNA complexes are indicated using a grey arrowhead. CepR2 supernatants were diluted serially in 3.16-fold increments in reactions with DNA fragments in the absence of OHL (gels 1–5). In gel 6, binding reactions containing CepR2 and Fragment 2 were amended with OHL to final concentrations of 0 μM, 0.032 μM, 0.1 μM, 0.315 μM, and 1.0 μM. C. Sequence of fragments containing the wild type CepR2 binding site (Fragment 2) or near-identical fragments having the indicated sequence alterations (Fragments 4 and 5). The dyad symmetrical CepR2 binding site is boxed, and altered sequences are underlined. Results are representative of at least two experiments with similar results.
