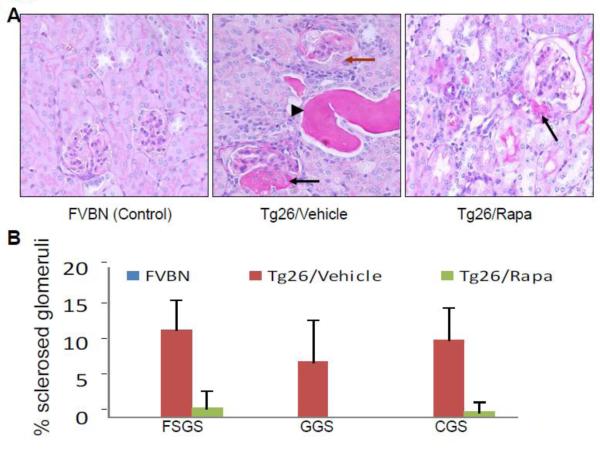
Figure 1. Rapamycin attenuates renal lesions in HIVAN mice.
Renal cortical sections from vehicle-receiving FVBN (control), vehicle-receiving Tg26 and Tg26-receiving Rapamycin (n=6) were stained with PAS and scored for severity of injury.
A. Representative microphotographs of cortical sections from a control, Tg26 and Tg26/Rapamycin (Tg26/Rapa) are displayed. Control mice displayed a normal glomerulus. Tg26 mice displayed dilated tubules with cast formation (indicated by a black arrowhead) segmental sclerosis (indicated by a black arrow) and collapsing sclerosis with proliferation of podocytes (indicated by a brown arrow). Tg26/Rapa revealed segmental sclerosis in occasional glomeruli (indicated by a black arrow).
B. Cumulative data showing percentage of segmentally sclerosed (SGS) globlally sclerosed (GGS) and collapsed sclerosed (CGS) glomeruli in renal cortical sections of FVBN, Tg6, and Tg26/Rapa mice.