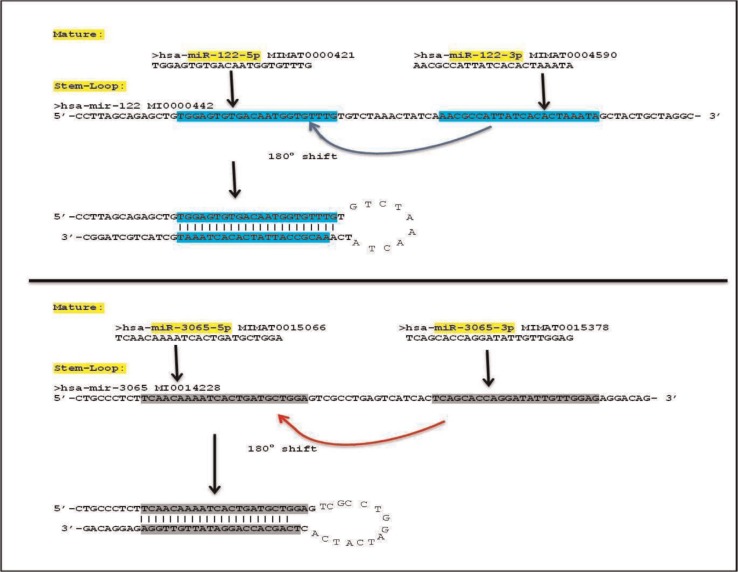
Fig. 1.
miRNAs are initially transcribed as several hundred nucleotide long primary or pri-miRNAs and are then processed to approximately 60-nucleotide (nt) hairpin pre-miRNAs in the nucleus by the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-specific ribonuclease (Drosha). The ribonuclease Drosha requires a dedicated dsRNA-binding protein to convert long, nuclear pri-miRNA transcripts into shorter pre-miRNA hairpin stem-loops. The pre-miRNAs are exported to cytoplasm where they are further excised by a RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) enzyme. These miRNAs are further processed into numerous specific 19 to 23 nt miRNAs, with the ability to target various endogenous and exogenous genes (8).