Fig 5.
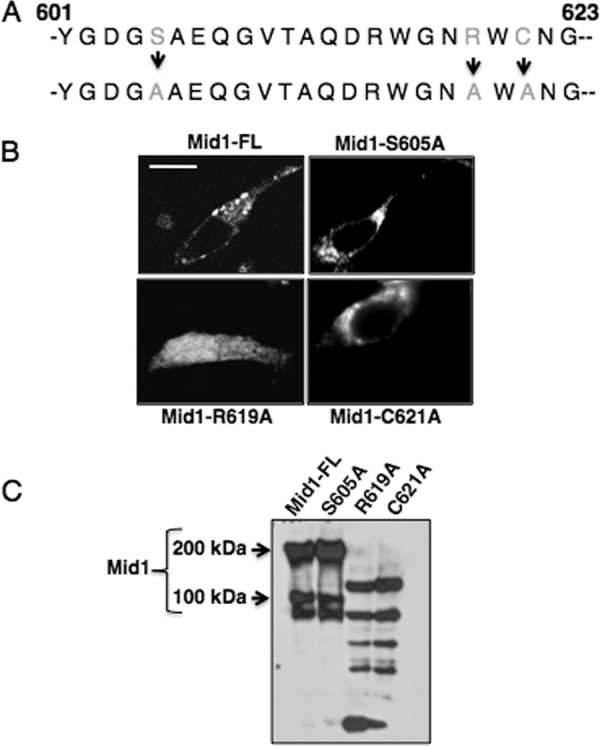
Arginine and cysteine residues of the modulatory region of Mid1 are critical for its localization. (A) Three key residues in the C-terminal modulatory region of Mid1 were altered. A predicted PKC-phosphorylation serine residue (Mid1-S605A), an arginine residue (Mid1-R619A), and a cysteine residue (Mid1-C621A) were substituted with alanine residues by PCR and confirmed by DNA sequencing. (B) GFP fusion proteins of the Mid1 point mutations were constructed and expressed in HEK293 cells under the control of the CMV promoter. Confocal microscopy revealed that the R619A Mid1 mutant displayed a diffuse localization pattern whereas the C621A mutant appeared to be localized in distinct patches throughout the cell. In contrast, the S605A mutant displayed a localization pattern similar to that of Mid1, suggesting predominant plasma membrane localization. (C) Biotin labeling of the HEK293 cells expressing the Mid1 point mutations further supported the notion of the absence of the R619A and C621A mutants from the cell surface and confirmed the unaltered targeting of S605A to the surface of HEK293 cells. Western blotting was performed using a commercial rabbit polyclonal antibody to GFP (1:5,000) as the primary antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, MA) followed by detection with a goat polyclonal antibody to rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) (1:5,000) (2).
