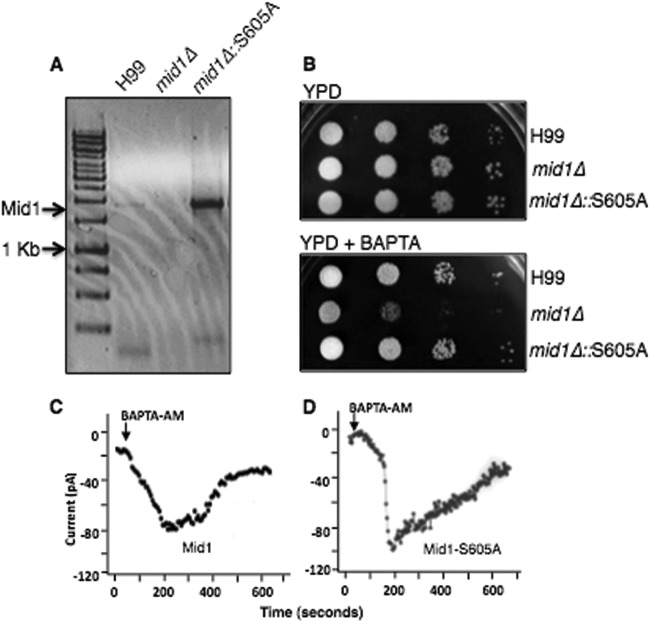
Fig 6.
A predicted phosphorylation site in the modulatory domain of Mid1 alters the kinetics of CMC activity. (A) The Mid1-S605A point mutation was expressed in the mid1Δ deletion strain of C. neoformans. Transcript analysis by reverse transcriptase PCR analysis revealed a robust expression of a transcript corresponding to the Mid1-S605A point mutation in C. neoformans. The S605A mutant was constitutively expressed under the control of the actin promoter. (B) Sensitivity assays demonstrated that the strain of C. neoformans expressing Mid1-S605A rescued the sensitivity of the mid1Δ strain on low-Ca2+ media (YPD plus 1 mM BAPTA; [Ca2+] = ∼100 nM), suggesting that serine 605 was not required for CMC activity. Strains H99, mid1Δ, and mid1Δ::S605A were grown overnight in YPD, serially diluted (104, 103, 102, 101), and spotted onto agar plates of YPD alone or YPD plus 1 mM BAPTA. (C and D) Representative traces of a time course of whole-cell Ca2+ currents through the Cch1 channel. Ca2+ currents were measured upon the depletion of Ca2+ stores by the addition of 10 μM BAPTA-AM in the patch pipette from HEK293 cells expressing Cch1 and full-length Mid1 (C) or expressing Cch1 and Mid1-S605A (D).