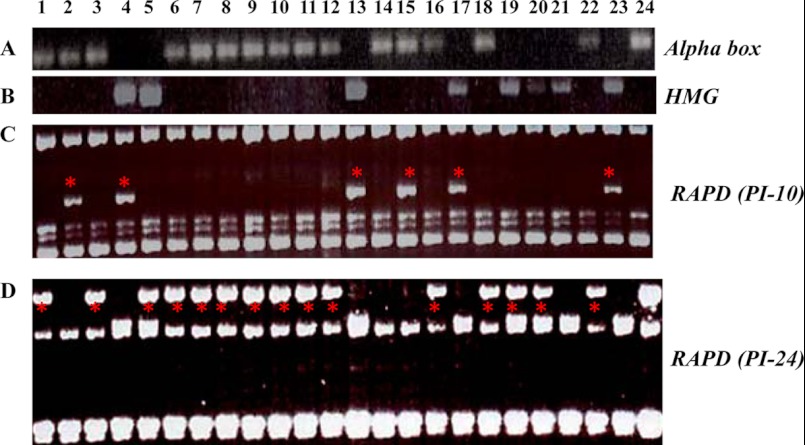
Fig 3.
(A and B) Mating-type determination of B. dermatitidis parental isolates (ATCC 18187 and ATCC 18188) and 22 potential progeny by PCR. Primers were designed to specifically amplify the alpha-box (plus mating type) and HMG (minus mating type) genes, which are characteristic of the B. dermatitidis MAT locus (see Table 1). (C and D) RAPD analysis of the progeny of isolates ATCC 18188 and ATCC 18187. Two RAPD primers, PI-10 (C) and PI-24 (D), reveal genetic variations (indicated by an asterisk) between these two parental isolates and the potential progeny. Lane 1, M1-1; lane 2, M1-2; lane 3, M1-3; lane 4, M1-4; lane 5, M1-5, lane 6, M1-6; lane 7, M1-7; lane 8, M1-8; lane 9, M1-9; lane 10, M1-10; lane 11, M2-1; lane 12, M2-2; lane 13, M2-3; lane 14, M2-4; lane 15, M2-6; lane 16, M2-7; lane 17, M2-11; lane 18, M2-16; lane 19, M2-17; lane 20, M2-18; lane 21, M2-19; lane 22, M2-20; lane 23, ATCC 18187; and lane 24, ATCC 18188.