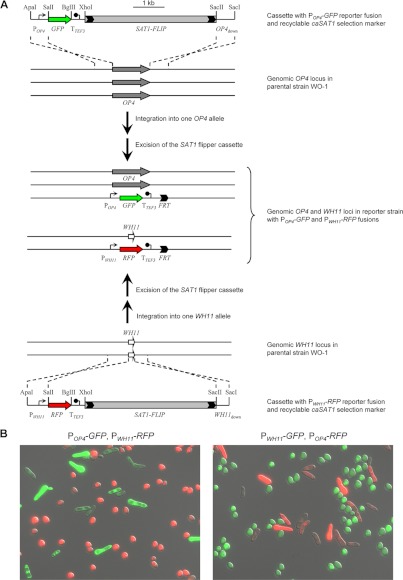
Fig 1.
Generation of phase-specifically labeled C. albicans strains. (A) Schematic of the sequential integration of POP4-GFP (top) and PWH11-RFP (bottom) reporter gene fusions into the genomic OP4 and WH11 loci of the parental wild-type strain WO-1 with the help of the recyclable SAT1 flipper cassette (SAT1-FLIP) to generate strains WOP4G42WH11R22A and -B (see also Table 1). Strains WOP4R22WH11G22A and -B, which contain POP4-RFP and PWH11-GFP reporter fusions, were generated in an analogous fashion. The parental strain WO-1 is trisomic for chromosome 1 and contains three copies of OP4, which is located on this chromosome (9). The genomic OP4 and WH11 coding sequences are indicated by the gray and white arrows, respectively; the cloned upstream (POP4 and PWH11) and downstream (OP4down and WH11down) sequences served for integration of the reporter cassettes into the respective genomic loci by homologous recombination. TTEF3, transcription termination sequence of the TEF3 gene; FRT, FLP recombination target sequence. Relevant restriction sites used for the generation of the reporter cassettes (see Materials and Methods) are indicated. (B) Phenotype of white and opaque cells of the reporter strains. Cells from white and opaque colonies of strains containing the indicated reporter fusions were mixed and observed by fluorescence microscopy. The pictures show an overlay of transmission and epifluorescence micrographs with GFP and RFP filter settings and demonstrate the phase-specific expression of GFP and RFP in white and opaque cells of the reporter strains. (Left) Strain WOP4G42WH11R22B; (right) strain WOP4R22WH11G22A.