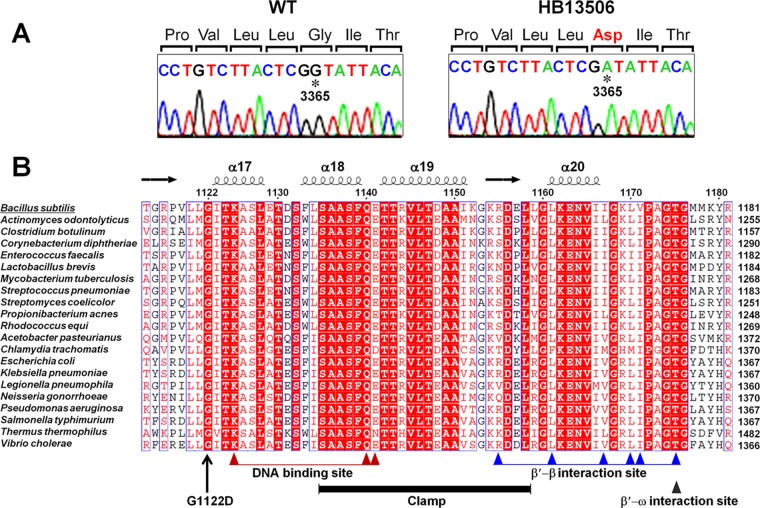
Fig 2.
Whole-genome resequencing and single-nucleotide polymorphism identification. (A) Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA confirms a G-to-A alteration at nucleotide 3365 of rpoC in strain HB13506 (as initially identified by Illumina whole-genome resequencing). The mutated residue is indicated by an asterisk, and the altered amino acid at position 1122 is shown in red. (B) Structure-based multiple-sequence alignment of the C-terminal domain of RpoC from B. subtilis (Swiss-Prot accession no. P37871), Actinomyces odontolyticus (A7B9Q3), Clostridium botulinum (A7FZ76), Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Q6NJF6), Enterococcus faecalis (Q82Z41), Lactobacillus brevis (Q03PV0), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (A5U053), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Q97NQ8), Streptomyces coelicolor (Q8CJT1), Propionibacterium acnes (G7U6X7), Rhodococcus equi (E9T446), Acetobacter pasteurianus (C7JFQ4), Chlamydia trachomatis (O84316), E. coli (P0A8T7), Klebsiella pneumoniae (B5XYF4), Legionella pneumophila (Q5X865), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Q5F5R6), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Q9HWC9), Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (P0A2R4), T. thermophilus (Q8RQE8), and Vibrio cholerae (Q9KV29). The absolutely conserved residues are boxed in red, and the highly conserved residues are represented by red letters. The secondary structure was adopted from the crystal structure of T. thermophilus RNAP (PDB ID 2O5J) (43). The conserved motifs were identified by using the NCBI Conserved Domain database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi) and by structural analysis of T. thermophilus RNAP (13).