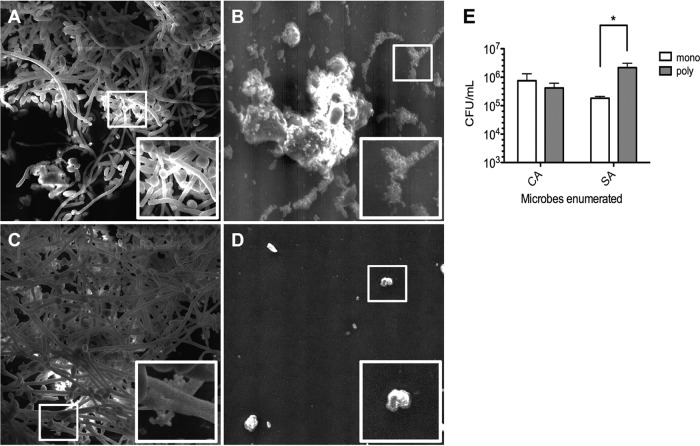
Fig 4.
SEM images of monomicrobial and polymicrobial biofilms on silicone disks. Analysis of silicone disk colonization by SEM demonstrated significant surface attachment by C. albicans (A) and S. aureus (B). (C) The polymicrobial biofilm showed numerous staphylococci attached to the biofilm components (hyphae and/or extracellular matrix) of C. albicans. (D) An uninoculated control is shown for reference. White boxes, zoomed areas of interest. Magnification, ×1,000. (E) Analysis of the numbers of CFU demonstrated that significantly more S. aureus cells could be recovered from silicone disks harboring polymicrobial biofilms (poly) than monomicrobial biofilms (mono). Error bars represent SDs. *, P < 0.05, using Student's t test.