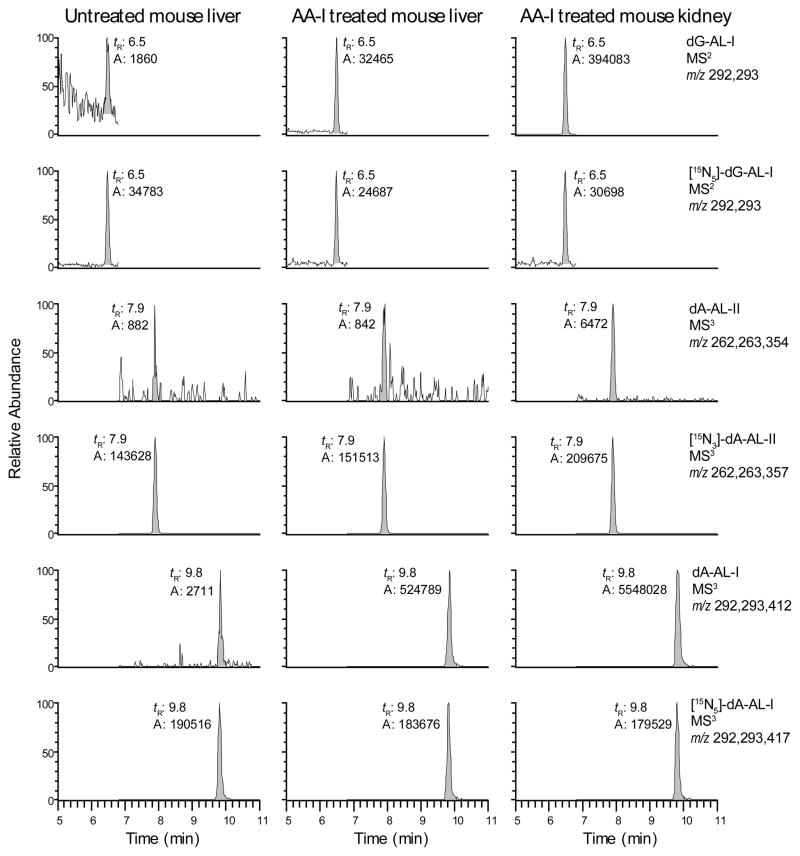
Figure 3.
The mass chromatograms of the AL-modified genomic DNA from a mouse dosed with AA-I (1 mg/kg). Mouse liver and kidney DNA were diluted with unmodified CT DNA by a factor of 10 and 5, respectively. The level of 15N-labeled internal standards was 5 adducts per 108 bases. The levels of AL-DNA adducts expressed per 108 bases in undiluted mouse liver and kidney were dG-AL-I: 58.1 (liver) and 300 (kidney); dA-AL-II: 0.7 (liver) and 0.8 (kidney); dA-AL-I: 176 (liver) and 1017 (kidney). The combined ions presented in the mass chromatograms of the adducts and internal standards were employed for quantitative measurements. The trace amounts of AL-DNA adducts detected in untreated DNA are attributed to the residual unlabeled dG and dA present in the isotopically labelled internal standards.