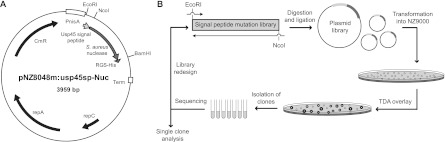
Fig 1.
Schematics of the expression constructs and screening process. (A) Plasmid map of pNZ8048m:usp45sp-Nuc, showing promoter PnisA, usp45 signal peptide sequence, S. aureus nuclease gene, and RGS-His tag in the modified pNZ8048 backbone (12). (B) Flow diagram of the mutagenesis and screening process. The signal peptide mutations were encoded by degenerate PCR primers. Nucleotide libraries were constructed, digested, and ligated into the pNZ8048m vector backbone via the EcoRI and NcoI sites. After plasmid transformation into L. lactis NZ9000, the resulting library was plated and screened by carefully overlaying a toluidine blue-DNA agar (TDA) mixture with inducer (10 ng/ml nisin) onto the agar plates. Since the size of the pink halo around each colony corresponds to the amount of nuclease secreted, clones could be quickly screened by eye and subjected to further analyses (sequencing, amylase secretion assays, Western blotting, etc.). Subsequent libraries were designed based on data collected in the initial screen.