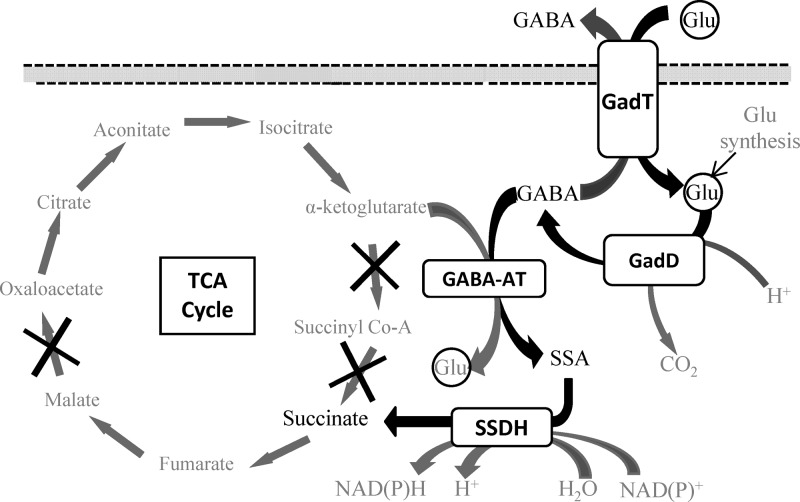
Fig 1.
Glutamate decarboxylase system and GABA shunt pathway of L. monocytogenes. Shown is the proposed model for the metabolism of GABAi in L. monocytogenes. Glui is decarboxylated to GABAi by GadD. The GABA can either be exported by GadT in exchange for another Glu or enter the GABA shunt pathway. Here GABAi donates its amino group to α-ketoglutarate via a transaminase enzyme (GABA-AT), resulting in the formation of SSA and Glui. The SSA is then oxidized to succinate by a dehydrogenase (SSDH). The incomplete TCA cycle of L. monocytogenes is shown, with the missing steps marked with an “X.” The GABA shunt pathway can provide an alternative source of succinate for the bacteria.