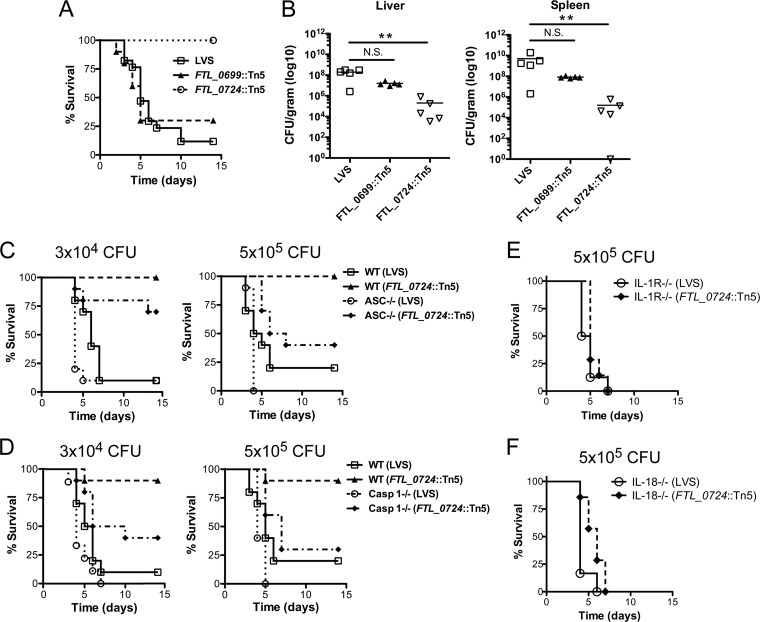
Fig 6.
The FTL_0724::Tn5 mutant was attenuated in vivo, whereas the FTL_0699::Tn5 mutant remained virulent. (A and B) WT C57BL/6 mice were infected i.p. with 3 × 104 CFU of the indicated strain of bacteria. (A) Mice were monitored for survival (n ≥ 10 mice per group). Results were pooled from two independent experiments. (B) At 3 days postinfection, bacterial burdens in liver and spleen were assessed (n = 5 mice per group). **, P ≤ 0.01; N.S., nonsignificant. (C and D) WT, ASC−/−, or caspase-1−/− mice (n ≥ 10 mice per group) were infected i.p. with either 3 × 104 CFU or 5 × 105 CFU of LVS or the FTL_0724::Tn5 mutant and monitored for survival. Results were pooled from two independent experiments. (E and F) IL-1RI−/− or IL-18−/− mice were infected i.p. with 5 × 105 CFU of LVS or the FTL_0724::Tn5 mutant and monitored for survival (n = 6 to 8 mice per group).