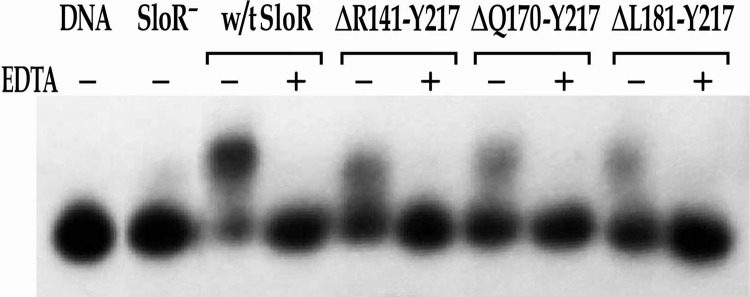
Fig 5.
Binding of wild-type SloR and its C-terminally truncated mutant variants to the sloABC promoter in EMSA. EMSAs were performed with a [γ-32P]ATP end-labeled 364-bp sloABC promoter-containing amplicon (the equivalent of 38 picograms) and whole-cell lysates containing 6.5 μg of total protein prepared from the GMS182 fusion strain and its derivatives. When appropriate, EDTA was added at a final concentration of 15 mM. Reaction mixtures were run on 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels and exposed for up to 48 h at −80°C in the presence of an intensifying screen. All three SloR deletion variants demonstrate reduced DNA binding (<40%) compared to wild-type SloR's binding. However, all retain some baseline affinity for DNA binding, suggesting that the FeoA domain, while important for DNA binding, does not appear to be a requirement for DNA binding.