Fig 1.
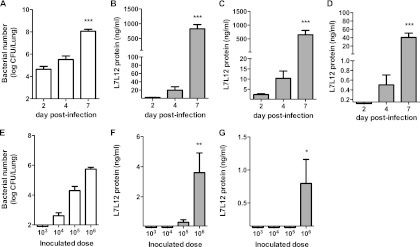
Effect of bacterial burden on RP-L7/L12 production in the pneumococcal pneumonia mouse model. (A to D) Bacterial numbers in the lungs were determined (A), and RP-L7/L12 production was measured in lung homogenates (B), urine (C), and serum (D) at days 2 (n = 10), 4 (n = 8), and 7 (n = 5) after infection of CBA/JN mice with S. pneumoniae at 106 CFU/ml. (E, F, and G) After 24 h of infection (n = 5) with various doses of S. pneumoniae in CBA/JN mice, bacterial numbers in lungs were determined (E), and RP-L7/L12 production was measured in lung homogenates (F) and urine (G). The results are expressed as means and SD. The limits of detection for ELISA measurement were 0.06 ng/ml in lung homogenates and 0.15 ng/ml in urine and serum. The asterisks denote significant differences (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001) compared to day 2 or 103 CFU/ml.
