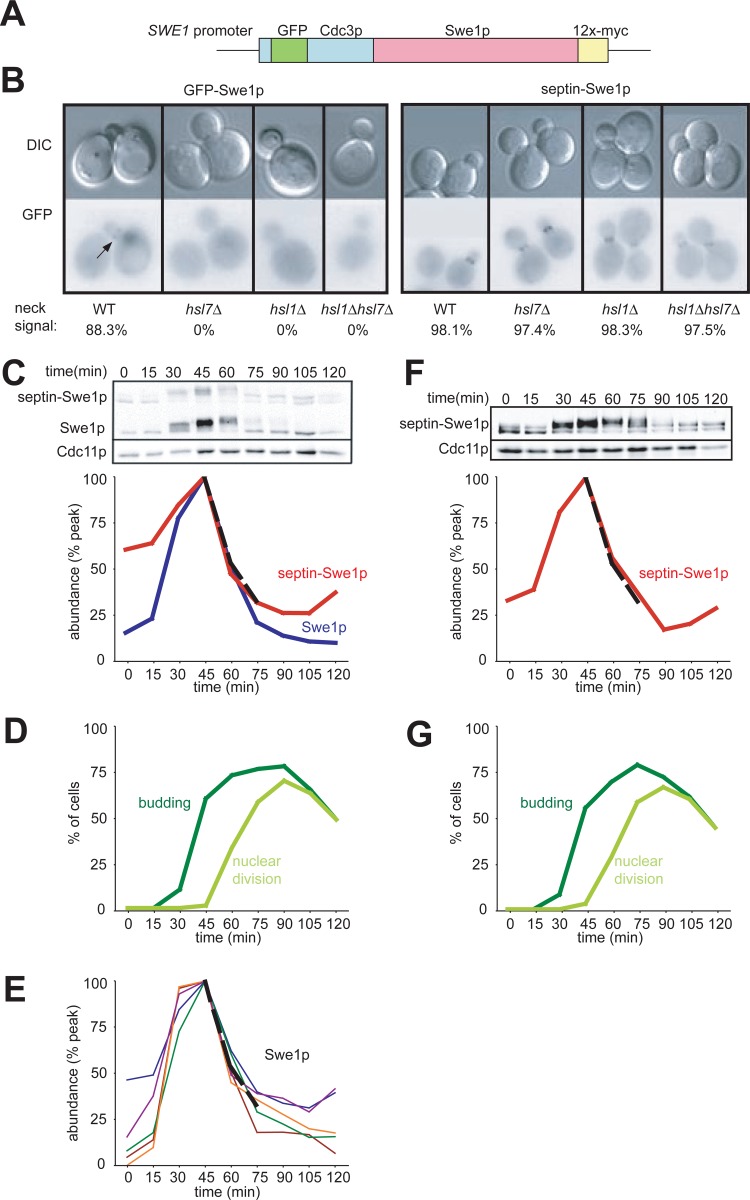
Fig 1.
Localization and degradation of a septin-Swe1p fusion. (A) Schematic of the Cdc3-GFP-Swe1p fusion protein. (B) Localization of Cdc3-GFP-Swe1p to the neck is independent of Hsl1p and Hsl7p. GFP-Swe1p is shown as a control. Cells were grown overnight at 30°C. Representative cells are shown, and over 200 cells of each strain were scored for bud neck signals. Strains containing GFP-Swe1p (with genotypes indicated in parentheses) were DLY12320 (wild type [WT]), DLY12369 (hsl7Δ), DLY12237 (hsl1Δ), and DLY12229 (hsl1Δ hsl7Δ), and strains containing Cdc3-GFP-Swe1p were DLY12321 (wild type), DLY12238 (hsl1Δ), DLY12370 (hsl7Δ), and DLY12230 (hsl1Δ hsl7Δ). (C) Swe1p and septin-Swe1p levels rise and fall in parallel as cells traverse the cell cycle. Cells containing both Swe1p-12×myc and septin-Swe1p-12×myc (DLY12321) were arrested in G1 phase with pheromone and released into fresh medium at 30°C to traverse the cell cycle. Pheromone was reintroduced 60 min after release to rearrest cells at the next G1 phase. Samples taken at 15-min intervals were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-myc antibody (Cdc11 as a loading control) and quantitated (graph). (D) Synchrony parameters (budding and nuclear division) for the experiment depicted in panel C were scored for >200 cells per sample. (E) Swe1p degradation kinetics are reproducible between experiments. Five replicates of the experiment depicted in panel C were quantified, and an average degradation profile for wild-type Swe1p is plotted as a dotted black line. (F) Degradation of septin-Swe1p occurs independent of wild-type Swe1p. A single-cycle synchrony experiment, as described above for panel C, was performed with swe1Δ strain DLY15563. (G) Synchrony parameters (budding and nuclear division) for the experiment depicted in panel F were scored for >200 cells per sample.