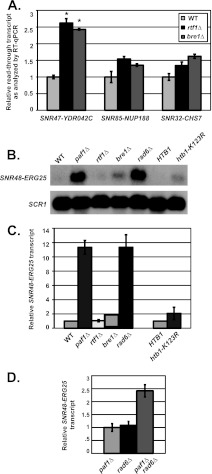
Fig 3.
snoRNAs require Rad6 but exhibit differential requirements for Rtf1-mediated H2B K123 monoubiquitylation. (A) Quantification of extended SNR47 (SNR47-YDR042C), SNR85 (SNR85-NUP188), and SNR32 (SNR32-CHS7) transcript levels in wild-type (KY2048), rtf1Δ (KY2277), and bre1Δ (KY2046) cells as determined by RT-qPCR, with the relative signal of wild-type cells set at 1. The SEMs are indicated by the error bars. Values that are significantly different (P value of <0.05) from the wild-type value are indicated by an asterisk. (B) Representative Northern blot analysis of extended SNR48 transcripts (SNR48-ERG25) in wild-type (KY1699), paf1Δ (KY1700), rtf1Δ (KY2041), bre1Δ (KY1713), rad6Δ (KY1712), hta2Δ htb2Δ (KY2043), and htb1-K123R hta2Δ htb2Δ (KY2044) cells. SCR1 transcript levels serve as a loading control. (C) Quantification of SNR48-ERG25 transcript levels performed as described above for panel B. For the four strains on the left side of the graph, the relative signal of wild-type (KY1699) cells was set at 1. The transcript levels in htb1-K123R hta2Δ htb2Δ cells (graph, right side) were made relative to the levels in hta2Δ htb2Δ (KY2043) cells. The SEMs are indicated by error bars. (D) Quantification of Northern blot analyses of extended SNR48 transcripts (SNR48-ERG25) in paf1Δ (KY1700), rad6Δ (KY1712), and paf1Δ rad6Δ (KY1378) cells. The relative signal of paf1Δ was set at 1, and the SEMs are indicated.