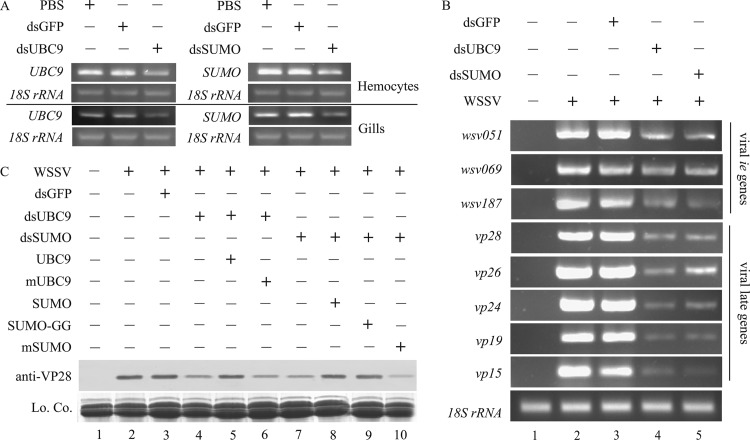
Fig 9.
WSSV late gene and protein expression was suppressed by knockdown of UBC9 and SUMO and rescued by injection of recombinant UBC9 and SUMO. (A) UBC9 and SUMO were knocked down in crayfish by RNA interference via oral delivery of E. coli expressing dsRNA. The crayfish were fed PBS or bacteria expressing dsRNA against GFP, UBC9, or SUMO every 24 h for 4 days. The efficiency of RNAi was confirmed in crayfish hemocytes and gills by RT-PCR using 18S rRNA as an internal control. (B) Viral gene expression, especially the expression of late genes, was inhibited when host UBC9 or SUMO was knocked down. Crayfish were infected with WSSV after the delivery of E. coli expressing dsRNA for 4 days, and hemocyte genomic DNA was extracted 48 h postinfection. Semiquantitative PCR was performed to quantify the expression of viral ie genes (wsv051, wsv069, and wsv187) and late genes (vp28, vp26, vp24, vp19, and vp15) using 18S rRNA as the control. (C) Reduced viral VP28 protein after knockdown of UBC9 or SUMO in crayfish was rescued by the injection of 50 μg recombinant UBC9 (lane 5), SUMO (lane 8), or SUMO-GG (lane 10) 0.5 h postinfection but not by the injection of mUBC9 (lane 6) and mSUMO (lane 10). Hemocyte proteins were extracted 48 h later and subjected to Western blotting for VP28. Lo. Co., loading control.