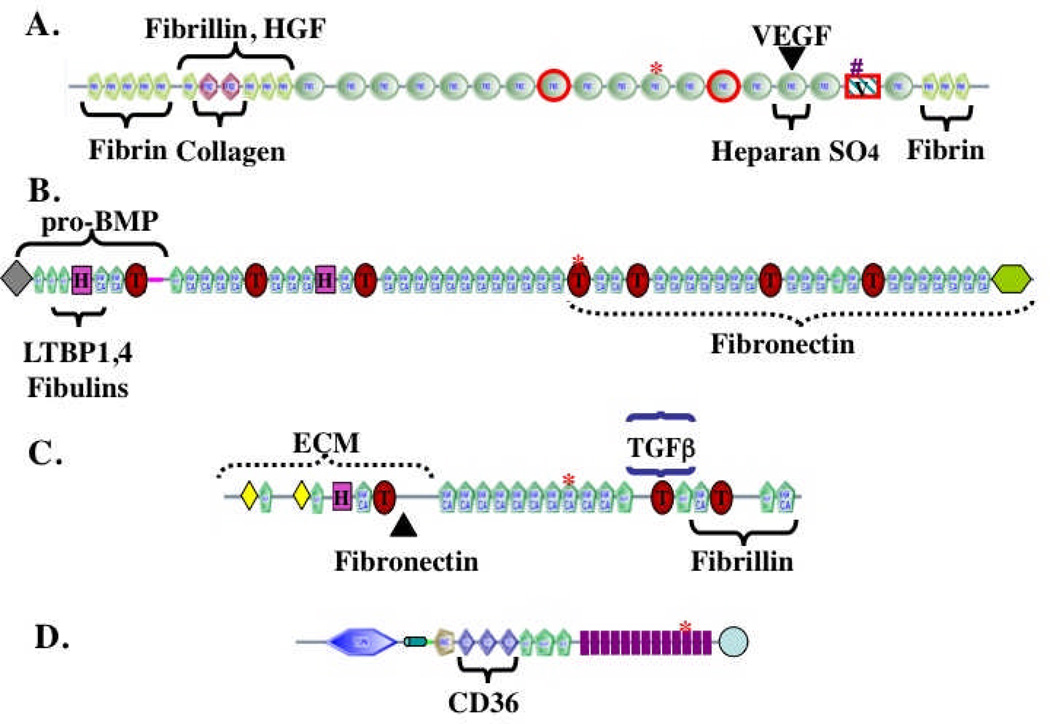
Figure 1. The complex domain structures of ECM proteins.
The figure shows representative ECM proteins (out of hundreds encoded in the genome). The proteins are built from multiple, independently folded domains, which occur in different combinations in different ECM proteins as a consequence of exon shuffling during evolution. The domain structures were generated from the SMART web site (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) and edited in light of specific knowledge about individual proteins.
A. Fibronectin. Encoded by a single gene but alternatively spliced at three regions (boxed in red) to generate 12 proteins in rodents and 20 in humans. FN3 domains are widespread in ECM proteins. Binding sites for other matrix proteins are marked. The heparan-sulfate-binding site can interact with proteoglyans (PGs) or with syndecan, an integral membrane PG. The RGD (arg-gly-asp) integrin-binding site is marked by a red asterisk and a second LDV (leu-asp-val) integrin-binding site is marked by a pound sign. Fibronectin is a proangiogenic molecule, whose function is compromised by elimination of the RGD site or of the two alternatively spliced FN3 domains36,37. FN also binds the proangiogenic growth factors VEGF and HGF16,17.
B. Fibrillin-1. A member of a three-gene family. Fibrillins are made up of EGF-like domains, which are found in many ECM proteins, as well as TB (TGFβ-binding, marked by T) and hybrid (H) domains that are both specific to fibrillins and LTBPs21,22. Known binding sites within fibrillin-1 for other matrix proteins and growth factors are marked.
C. LTBP-1. A member of a four-gene family with structure related to that of fibrillins. Known binding sites for TGFβ/LAP latent complex and for fibrillin and fibronectin are marked.
D. Thrombospondin-1. Member of a five-gene family38. Thrombospondins 1 and 2 have the structure shown and both are antiangiogenic. Antiangiogenic activity lies in the TSP1 repeats, which bind to the CD36 receptor. TSP1 repeats are also found in other ECM proteins. Thrombospondins also contain EGF-like repeats and a VWC domain, known in other proteins to bind BMPs. The 13 TSP3 repeats (purple) and C-terminal domain are unique to thrombospondins and bind multiple Ca++ ions.
In all proteins, the asterisks mark RGD (arg-gly-asp) tripeptide sequences that may bind to integrins, as is well documented for the similar motif in fibronectin (see A).