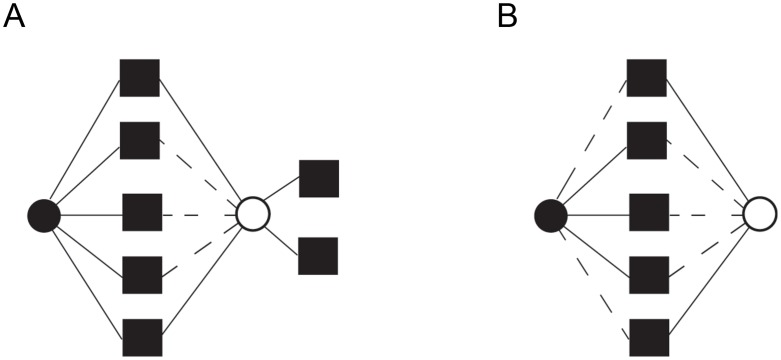
Figure 3. Distinct functional fates for genes duplicated by small-scale duplication (SSD) and whole-genome duplication (WGD).
(A) After the duplication of a gene by SSD (circles), one of the gene copies (black circle) maintains the ancestral functions (squares), while the other (white circle) loses (discontinuous lines) some ancestral functions while establishing novel genetic interactions (functions) through the process of neo-functionalization. (B) Genes duplicated by WGD sub-functionalize through the partitioning of ancestral functions so that each gene copy specializes in a subset of the ancestral functions.