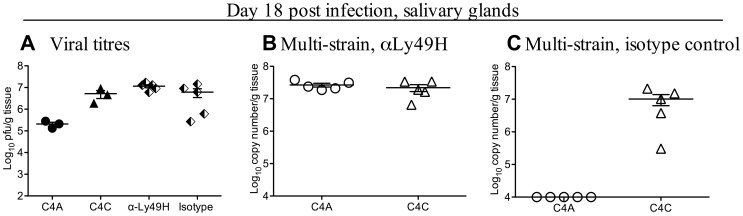
Figure 5. Blocking the NK cell receptor Ly49H eliminates viral competition.
B6 mice were treated with 200 µg of the monoclonal antibody 3D10 (anti-Ly49H) or 200 µg of isotype control antibody 9E10 (anti-cMyc) on day −2, 0, 4, 8, 12 and 16 of infection. On day 0 mice were inoculated i.p. with 1×104 pfu of either a single MCMV strain (closed symbols) or a total of 1×104 pfu of a mixed inoculum of C4A and C4C (half filled diamonds - plaque assay or open symbols – strain specific PCR). A. Titers of infectious virus were determined by plaque assay in salivary glands of B6 mice infected with either C4A or C4C (closed symbols), or in anti-Ly49H or isotype control treated mice that were also co-infected with C4A and C4C (half filled diamonds). B. Viral DNA levels in B6 mice treated with anti-Ly49H and co-infected with C4A and C4C. Note both C4A and C4C DNA were detectable following anti-Ly49H treatment. C. Viral DNA levels in B6 mice treated with isotype control mAb and co-infected with C4A and C4C. Note competition was retained in these mice with C4A undetectable in the salivary glands. The x-axis represents the limit of detection for plaque assays (100 pfu/g of tissue) and the multiplex qPCR (1×104 copy number/g of tissue), n = 5 co-infected mice/group, 3 single strain infected mice/group.