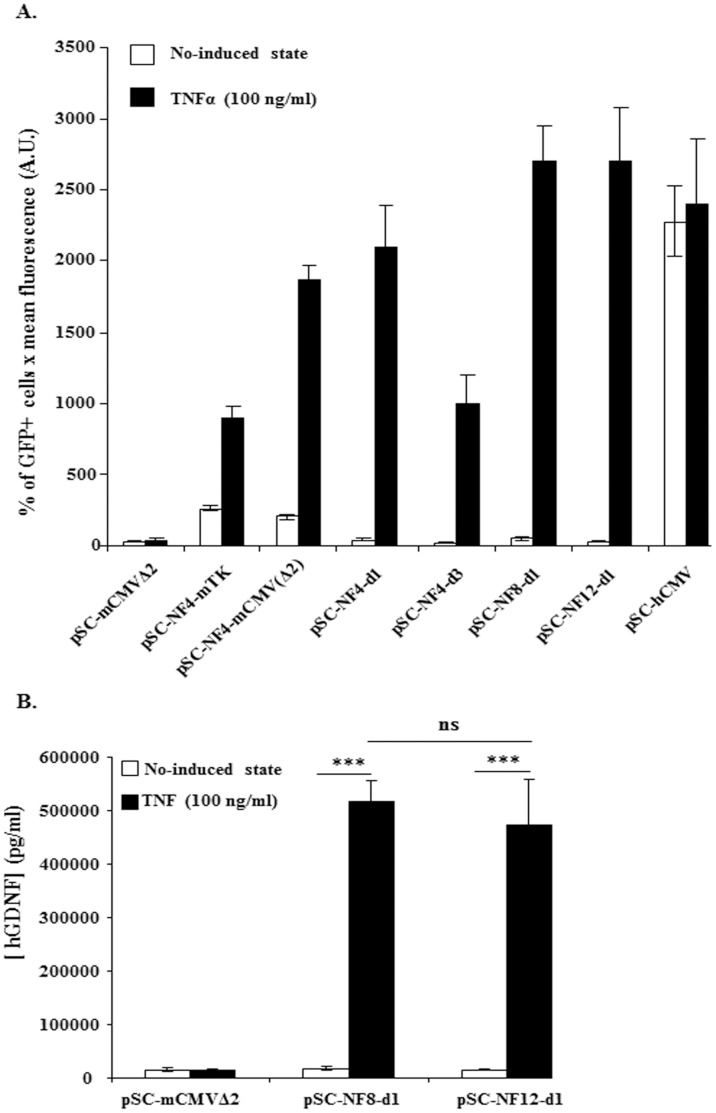
Figure 2. In vitro TNFα-mediated induction of NF-κB-responsive AAV vectors.
HEK-293T cells were transfected with AAV-NF-EGFP (A) or with AAV-NF-hGDNF (B) vectors using the calcium phosphate coprecipitation method. 5×105 cells in 6-wells were transfected with 250 ng DNA. Forty-eight hrs later, transfected cells were treated or not with TNFα (100 ng/ml) for 5 hrs. HEK-293T transfected with AAV-NF-EGFP were analyzed for GFP expression on a FACStar analyser/sorter (Becton Dickinson) (A). To analyse the inducibility of AAV-NF-hGDNF vectors in HEK-293T, the supernatant were harvested 4 h after changing the medium to measure secreted GDNF concentrations by a commercial ELISA assay (Human GDNF CytoSets, catalog #CHC2423, BioSource, Nivelles,Belgium) (B). For both AAV-NF8-d1-hGDNF and AAV-NF12-d1-hGDNF vectors, the differences between the TNFα-treated and untreated cultures were highly significant. The differences between the basal levels and the induced levels for AAV-NF8-d1-hGDNF versus AAV-NF12-d1-hGDNF are not significant (B). (***, p<0.001; ns, p>0,05, one-way ANOVA Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison Test). Data are from one representative out of three experiments (3 separate transfections). Bars represent means ± standard deviations (SD) (A) or means ± standard error of the means (SEM) (B) from triplicate wells. A.U., arbitrary units.