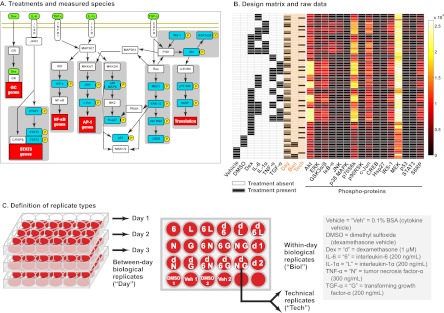
Fig. 1.
Experimental design and raw data. A, A schematic view of the experiment. We investigated the cell signaling network of HepG2 cells by treating the cells with combinations of the ligands (green) including the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1α (IL-1α), the glucocorticoid hormone analog dexamethasone (Dex) and the growth factor transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α). We used multiplexed bead-based immunoassays to measure the levels of phospho-proteins (blue) that function in intracellular signaling. The full names of the phospho-proteins are listed in the Materials and Methods section. B, Design matrix and raw data. The design matrix (at left) is shown with the columns pertaining to the replicate types, defined in panel C, shaded in orange. The filled boxes indicate the samples for which the corresponding treatments were applied. For the Day column, the unfilled boxes denote Day 1, the boxes filled gray denote Day 2 and the boxes filled black denote Day 3. The raw data is presented on the right as a heat map with one column for each of the 16 phospho-protein analytes and each row representing a single replicate of a particular condition. The colors represent MFI values spanning 68 to 26,103. C, Definition of replicate types. Our experiment featured three types of replicates: (1) Between-day biological replicates (“Day”), which we defined as cells independently treated with the same experimental perturbation but on different days (batches), (2) Within-day biological replicates (“Biol”), which we defined as cells independently treated with the same experimental perturbation on the same day (i.e. in the same batch), and (3) Technical replicates (“Tech”), which we defined as biological samples that were divided and pipetted into separate wells in the Bio-Plex assay plate. These replicate types are subject to different types of variance: Technical replicates are subject to variance introduced in the assay process, within-day biological replicates are subject to both assay variance and variance introduced by the act of experimentally manipulating the cells and between-day biological replicates are subject to the previous sources of variance in addition to batch effects.