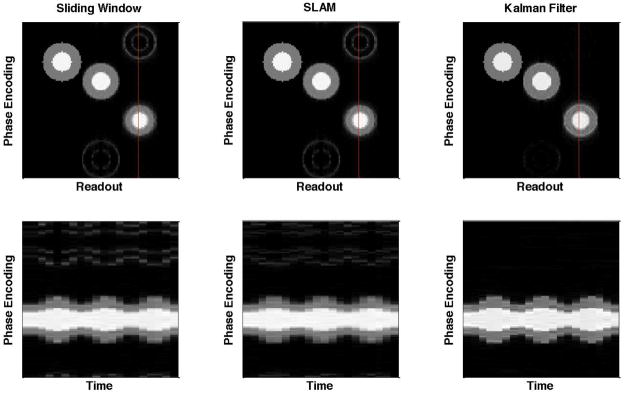
Figure 1.
Numerical phantom study. The reconstructed images (top row) and the image intensities along the red vertical line versus time (bottom row) using the sliding window, SLAM and Kalman filter methods. The three pairs of concentric circles are with fixed radius, slowly oscillating radius and rapidly oscillating radius (from left to right). The Kalman filter method substantially reduces aliasing and temporal blurring. The reduction in temporal blurring can be seen in the sharper temporal response and the reduced blurring of the boundaries between regions of the phantom.