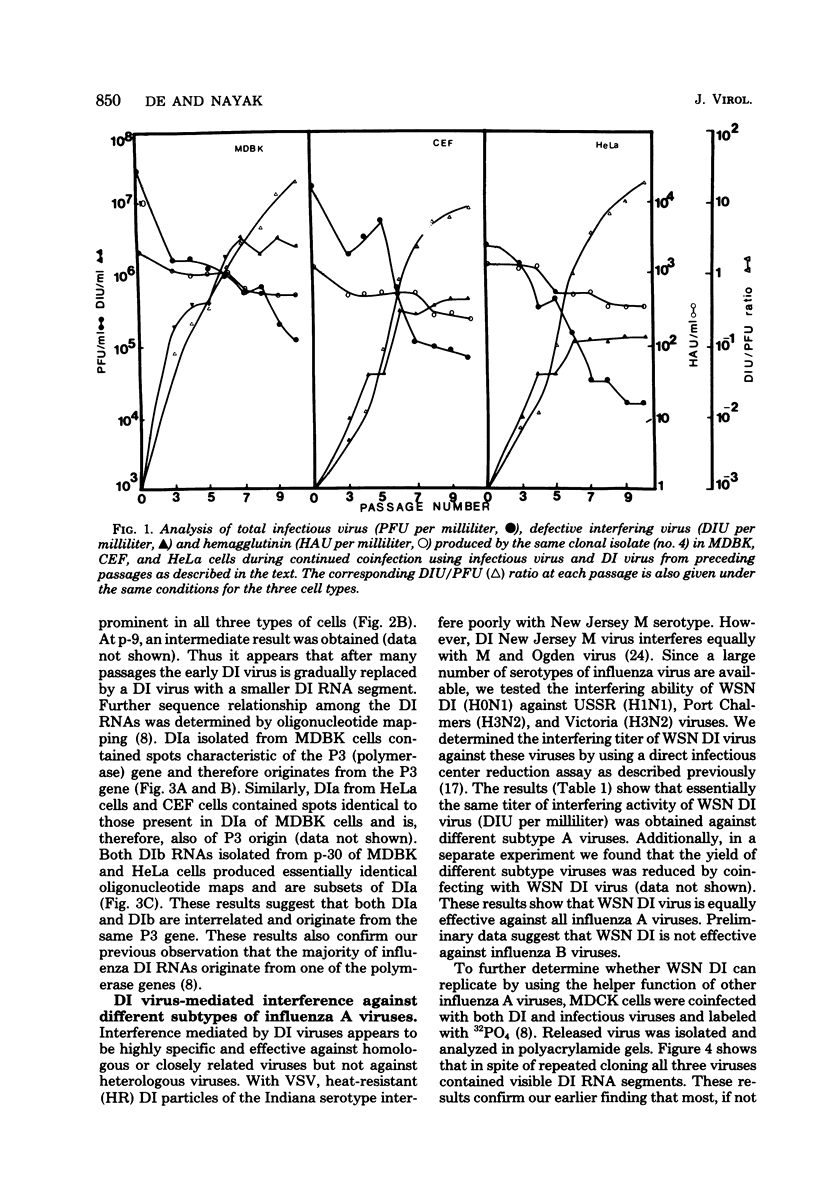
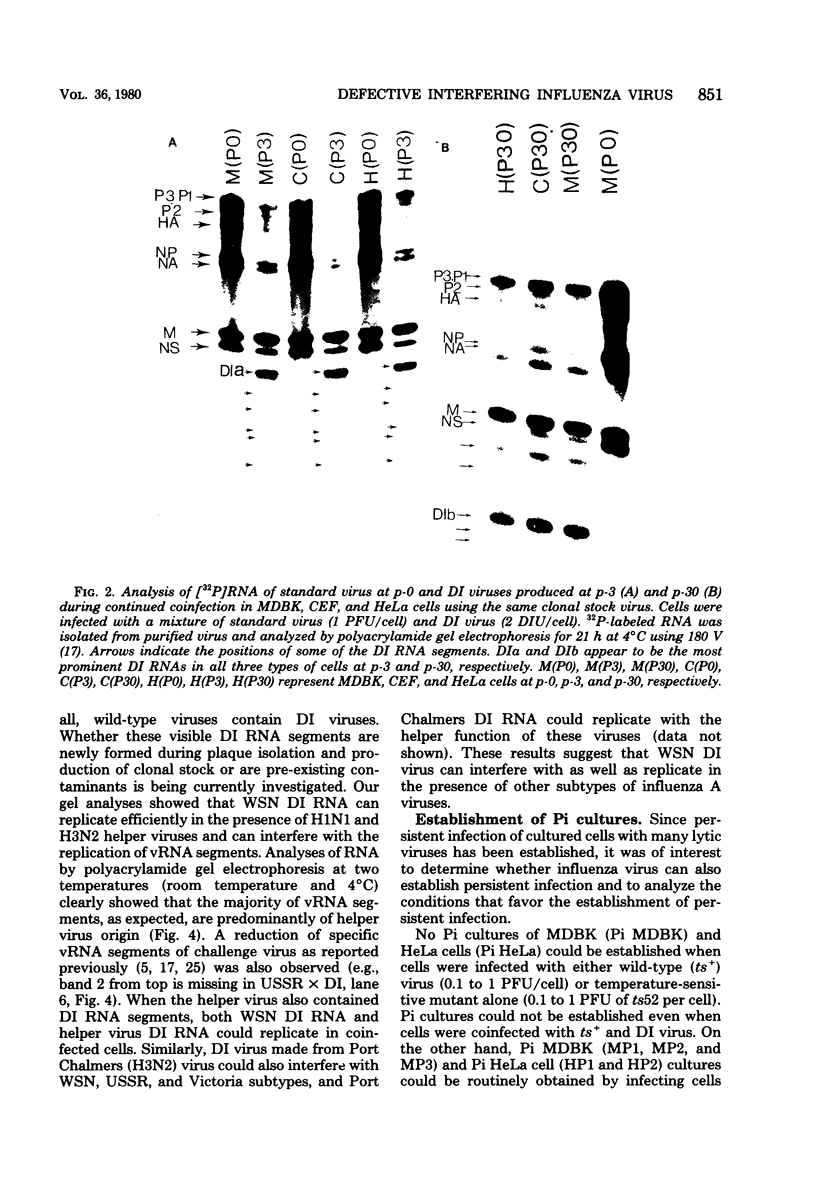
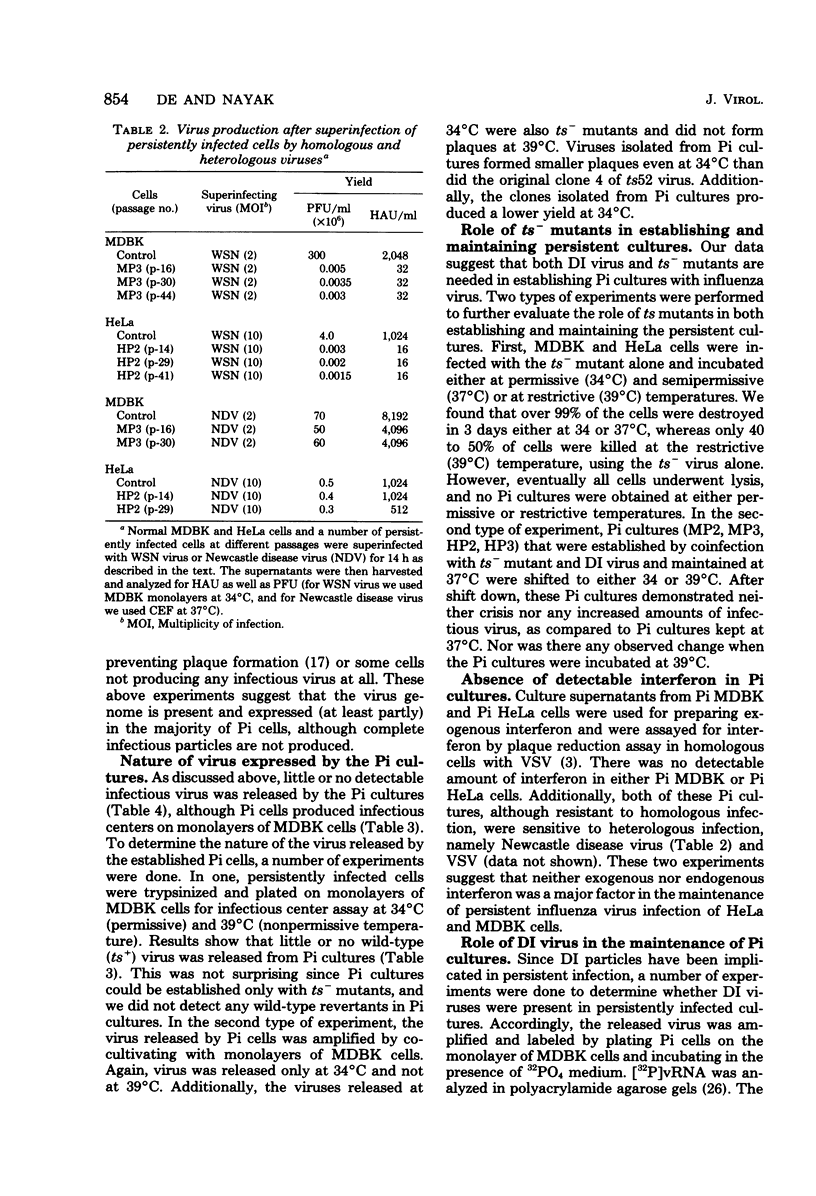
Abstract
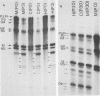
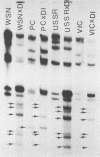
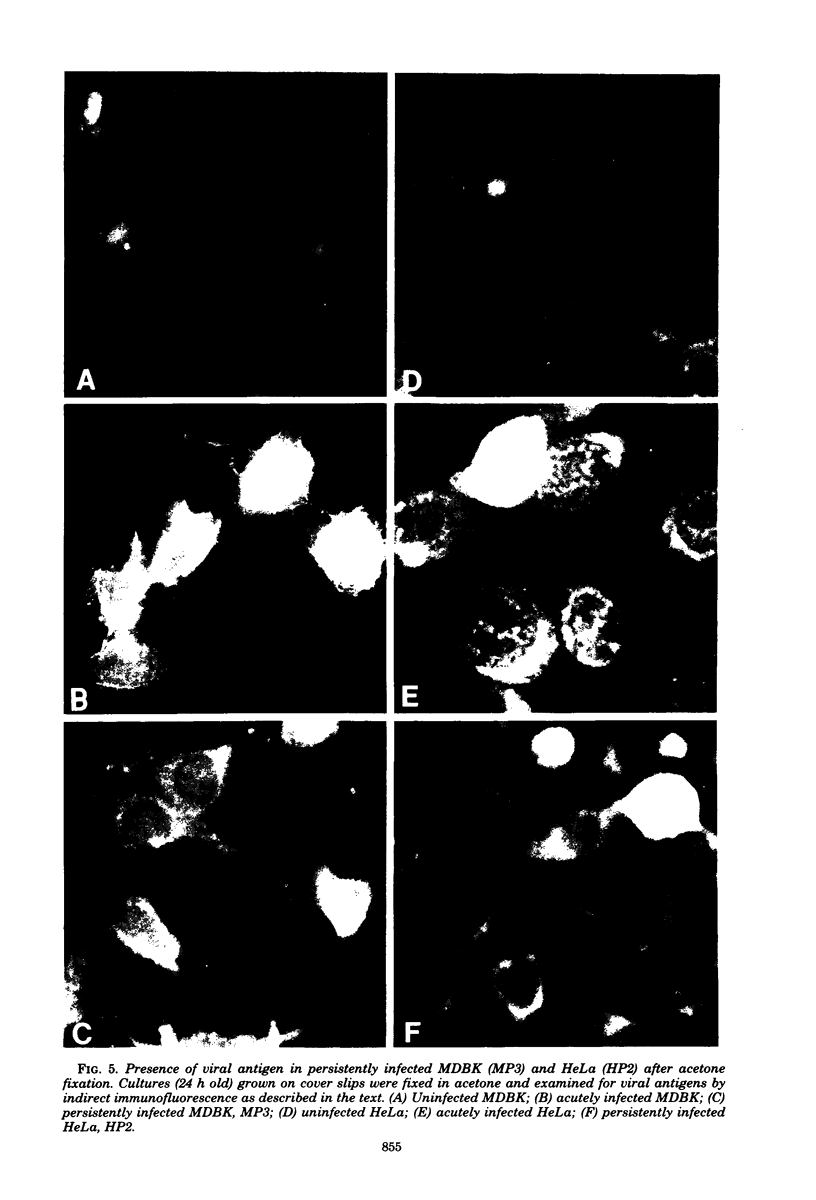
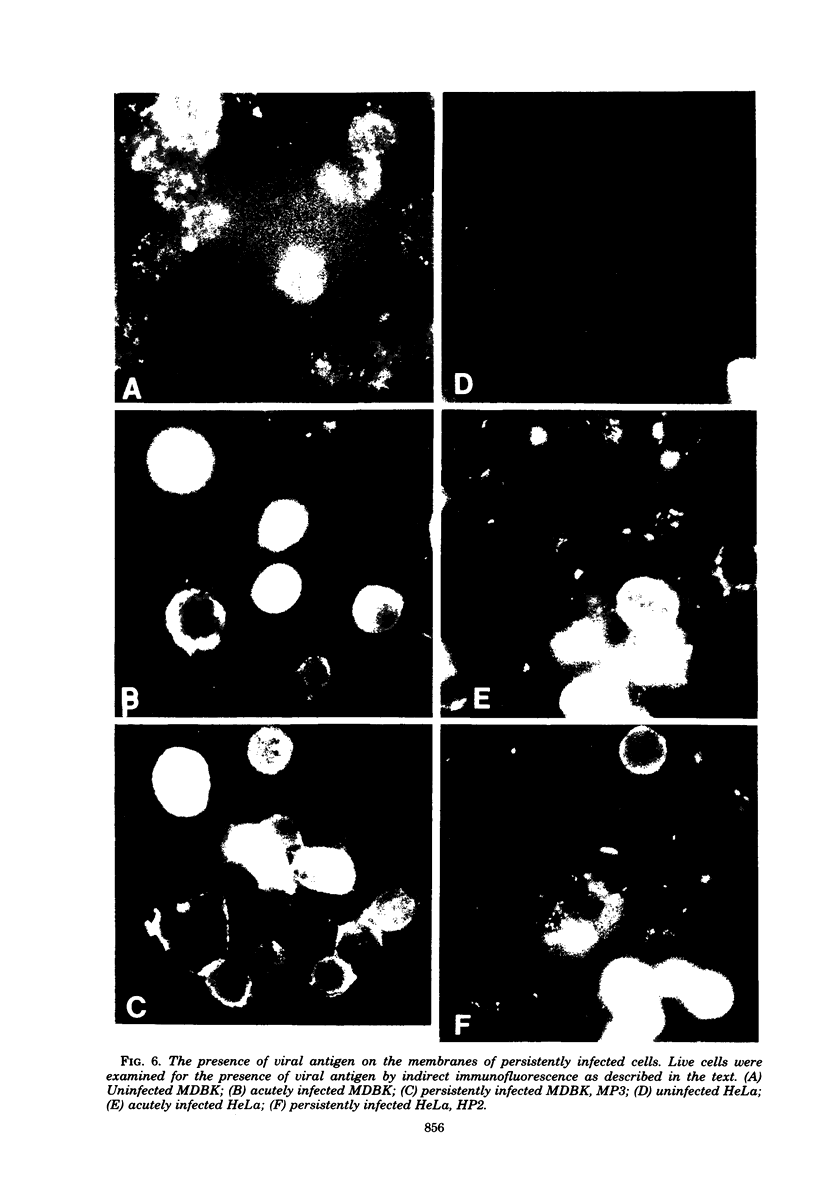
WSN (H0N1) influenza virus upon undiluted passages in different species of cells, namely, bovine kidney (MDBK), chicken embryo (CEF), and HeLa cells, produced a varying amount of defective interfering (DI) virus which correlated well with the ability of the species of cell to produce infectious virus. However, the nature of the influenza DI viral RNA produced from a single clonal stock was essentially identical in all three cells types, suggesting that these cells do not exert a great selective pressure in the amplification of specific DI viral RNAs either at early or late passages. DI viruses produced from one subtype (H0N1) could interfere with the replication of infectious viruses belonging to other subtypes (H1N1, H3N2). DI viral RNAs could also replicate with the helper function of other subtype viruses. The persistent infection of MDBK and HeLa cells could be initiated by coinfecting cells with both temperature-sensitive mutants (ts-) and DI influenza viruses. Persistently infected cultures cultures at early passages (up to passage 7) showed a cyclical pattern of cell lysis and virus production (crisis), whereas, at later passages (after passage 20), they produced little or no virus and were resistant to infection by homologous virus but not by heterologous virus. The majority of persistently infected cells, however, contained the complete viral genome since they expressed viral antigens and produced infectious centers. Selection of a slow-growing temperature-sensitive variant rather than the presence of DI virus or interferon appears to be critical in maintaining persistent influenza infection in these cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Graham A. F. Persistent infections in L cells with temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):250–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.250-262.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almond J. W. A single gene determines the host range of influenza virus. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):617–618. doi: 10.1038/270617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Holmes K. V. Host-dependent restriction of influenza virus maturation. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W., Pons M. W. The RNAs of infective and incomplete influenza virions grown in MDBK and HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpton W. M., Dimmock N. J., Minor P. D., Avery R. J. The RNAs of defective-interfering influenza virus. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):370–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Hiti A. L., Nayak D. P. Influenza defective interfering viral RNA is formed by internal deletion of genomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):215–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. Sequence relationships among defective interfering influenza viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. W., Stone M. P., Joklik W. K. Separation of single-stranded ribonucleic acids by acrylamide-agarose-urea gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):599–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Ramseur J. M. Mechanisms of persistent infections by cytopathic viruses in tissue culture. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1979;60(2):83–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01348025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Grabau E. A., Jones C. L., Semler B. L. Evolution of multiple genome mutations during long-term persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Breindl M. Factors involved in the generation and replication of rhabdovirus defective T particles. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):805–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.805-815.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Semmel M., Huppert J. Host-range mutant of fowl plague virus (FPV): comparison of the genome and virus proteins. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):503–509. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P., De B. K. Diversity and generation of defective interfering influenza virus particles. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Nayak D. P. Defective influenza viral ribonucleoproteins cause interference. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):697–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.697-702.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Glimp T., Clewley J. P., Bishop D. H. Studies on the generation of vesicular stomatitis virus (indiana serotype) defective interfering particles. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):142–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai A., Matsumoto S., Tanabe K. Characterization of rabies viruses recovered from persistently infected BHK cells. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):520–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Kennedy S. I. Semliki forest virus persistence in mouse L929 cells. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):141–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90560-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Ueda M., Sugiura A. Origin of small RNA in von Magnus particles of influenza virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1142–1148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1142-1148.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P. Defective interfering influenza viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:619–644. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.003155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Tobita K., Janda J. M., Davis A. R., De B. K. Homologous interference mediated by defective interfering influenza virus derived from a temperature-sensitive mutant of influenza virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):375–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.375-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Schulman J. L. Differences in RNA patterns of influenza A viruses. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):876–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.876-884.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu M., Lehmann-Grube F. Defective interfering particles in mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):78–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., Davidson W. B., Martin S. J. The role of defective interfering particles in persistent infection of Vero cells by measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):89–97. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Holland J. J. Role of defective interfering particles of Sendai virus in persistent infections. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C., Blair C. D. Persistent infection of cultured mammalian cells by Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):580–589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.580-589.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Koennecke I., Rott R. Host range recombinants of fowl plague (influenza A) virus. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Murphy B. R. Host range mutants of an influenza A virus. Arch Virol. 1978;58(4):323–333. doi: 10.1007/BF01317824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. L., Palese P. Virulence factors of influenza A viruses: WSN virus neuraminidase required for plaque production in MDBK cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.170-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Holland J. J. Persistent vesicular stomatitis virus infection mediates base substitutions in viral RNA termini. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):420–428. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.420-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark C., Kennedy S. I. The generation and propagation of defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest virus in different cell types. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON MAGNUS P. Incomplete forms of influenza virus. Adv Virus Res. 1954;2:59–79. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Rosenthal R., Schlesinger S. Establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sindbis virus in BHK cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):463–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.463-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Burner P. A., Holland J. J., Oldstone M. B., Thompson H. A., Villarreal L. P. A comparison of biochemical and biological properties of standard and defective lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(4-6):403–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Desselberger U., Palese P. Evolution of human influenza A viruses in nature: sequential mutations in the genomes of new H1N1. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Quagliana D. O. Temperature-sensitive mutants isolated from hamster and canine cell lines persistently infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1332-1336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wachter R., Fiers W. Preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 32 P-labeled RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Sep;49(1):184–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]