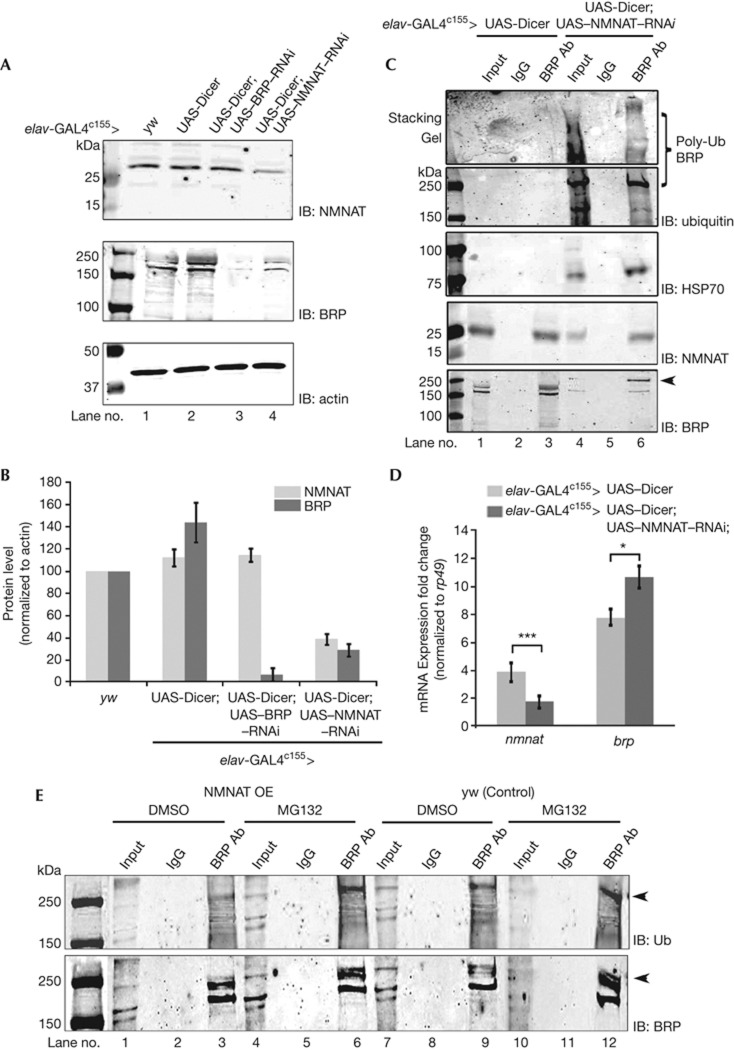
Figure 2.
Reduction in NMNAT level causes BRP ubiquitination and aggregation. (A) Western analysis of brain lysates from flies overexpressing UAS-Dicer or UAS-Dicer; UAS–NMNAT–RNAi reveals that BRP level is down regulated with a reduced level of NMNAT in NMNAT RNAi brains; however, the NMNAT level is unchanged in BRP RNAi brains. (B) Quantification of the protein level of NMNAT and BRP in A. n=3. All data were presented as mean±s.e.m. (C) Immunoprecipitation of brain lysates from flies overexpressing UAS-Dicer or UAS-Dicer; UAS–NMNAT–RNAi with BRP antibody reveals significant ubiquitination of BRP in NMNAT–RNAi brains, including poly-ubiquitinated BRP (marked by square bracket). Ubiquitinated BRP also recruits HSP70 and remaining NMNAT. BRP ubiquitination is further shown by an upshifted band detected with anti-BRP (marked by arrowhead) in NMNAT–RNAi brain. (D) Real-time PCR shows that nmnat transcript is reduced, while brp transcript is slightly increased in NMNAT-knockdown flies, compared with flies overexpressing UAS-Dicer. All data were presented as mean±s.e.m. Significance level was established by t-test. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, n=3. (E) MG132 treatment induces ubiquitination of BRP. One day after eclosion flies were fed with 50 μM MG132 or DMSO for 24 h and brain lysate was prepared immediately after drug feeding. Multiplex western analysis was carried out with anti-BRP and anti-ubiquitin antibodies and respective IRDye 700DX- and IRDye 800DX-conjugated secondary antibodies. Ubiquitinated BRP is marked by arrowheads. BRP, Bruchpilot; DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; IB, immunoblotting; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; RNAi, RNA interference; Ub, ubiquitin.