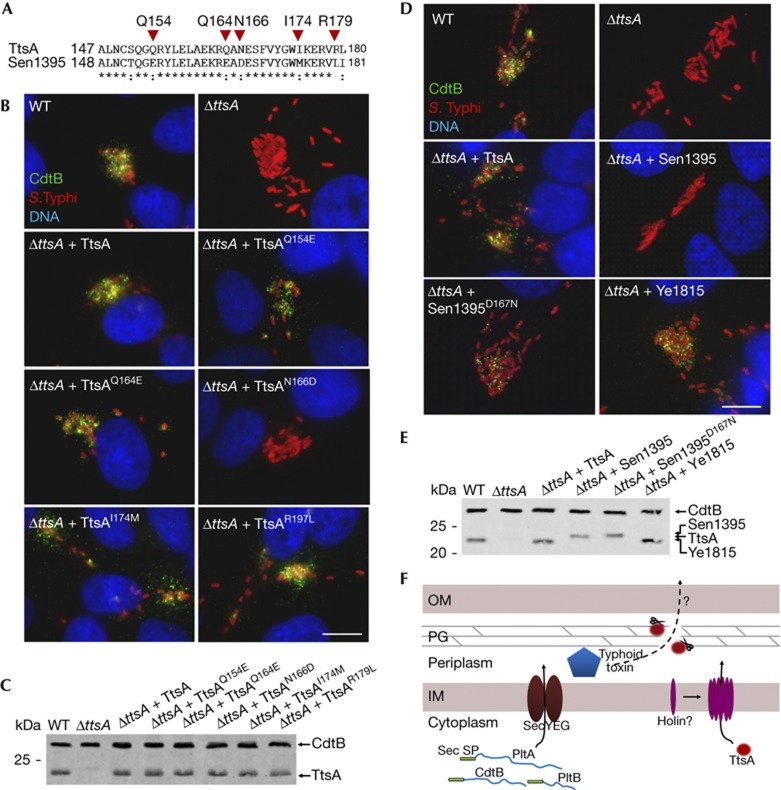
Figure 5.
A C-terminal region of TtsA determines its ability to secrete typhoid toxin. (A) Amino-acid sequence comparison of the C terminus of TtsA and Sen1395. The residues mutated in this analysis are indicated. (B) Mutagenesis analysis of the C-terminal region of TtsA. Henle-407 cells were infected with WT S. Typhi or a ΔttsA mutant derivative expressing chromosomally encoded FLAG-tagged cdtB and carrying plasmids encoding the indicated TtsA mutant proteins. Twenty-two hours post infection, infected cells were fixed and stained with a mouse monoclonal antibody directed to the FLAG epitope (to visualize CdtB), a rabbit antibody directed to S. Typhi LPS and DAPI for DNA detection. The bar represents 10 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of the expression levels of the indicated proteins in the strains used in panel (B). (D) The N166 residue of TtsA is crucial for typhoid toxin secretion. Henle-407 cells were infected with WT S. Typhi or a ΔttsA mutant derivative expressing chromosomally encoded FLAG-tagged cdtB and carrying plasmids encoding the indicated proteins. Twenty-two hours post infection, infected cells were fixed and stained with a mouse monoclonal antibody directed to the FLAG epitope (to visualize CdtB), a rabbit antibody directed to S. Typhi LPS and DAPI for DNA detection. The bar represents 10 μm. (E) Western blot analysis of the expression levels of the indicated proteins in the strains used in panel (D). (F) Typhoid toxin secretion model. Typhoid toxin components PltA, PltB and CdtB have an N-terminal Sec signal peptide, which mediates their export to the periplasm through the Sec machinery. Further protein export requires enzymatically active TtsA, which lacks a canonical N-terminal signal peptide and therefore must be exported to the periplasm by a yet unidentified holin. Sec signal peptides (Sec SP), PG, IM and OM are indicated. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; IM, inner membrane; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; OM, outer membrane; PG, peptidoglycan; WT, wild-type.