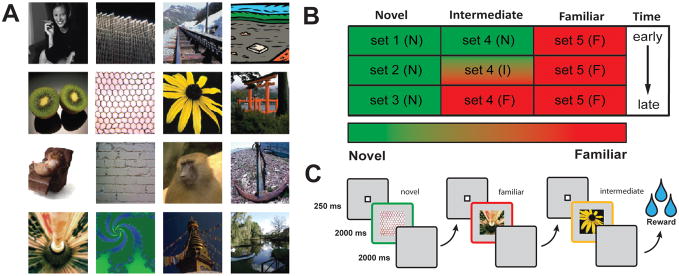
Figure 1. Visual Stimuli and VARNOV task structure.
A. Example of visual stimuli used in the Variable Novelty (VARNOV) task. Images were collected and modified from a wide range of sources and adjusted to be 300×300 pixels (or 10 DVA) in size. Stimuli were presented in the center of the display and monkeys were free to explore the images after stimulus onset. B. Diagram of the familiarity gradients inherent in the VARNOV task. Note that the “Novel” category consists of 3 sets of unique images. Once images in this category are no longer novel (i.e., after 5 presentations), images are refreshed with stimuli from another set until all novel images are exhausted. Novel and familiar contrasts are measured between images in columns 1 and 3 as well as between early and late trials in column 2. C. Example of one VARNOV trial, one image from each category is presented. After three image presentations subjects receive a small juice reward. Image order is randomized so no specific association can be made with respect to reward delivery.