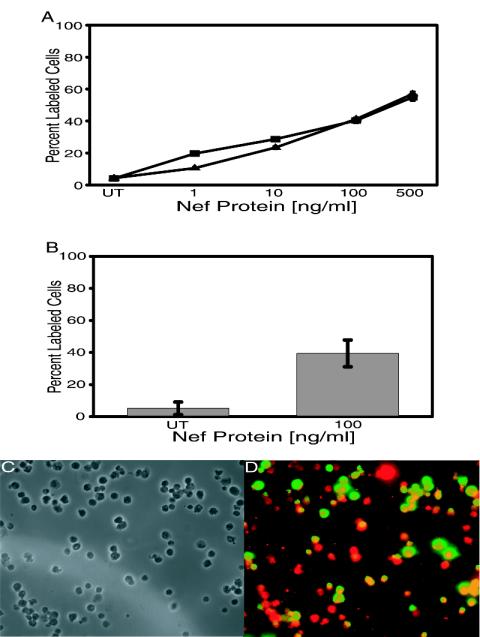
FIG. 1.
Nef-induced apoptosis as measured by dose response in lymphocytic cells. (A) Jurkat or H9 cell cultures were untreated or were treated with 1, 10, 100, or 500 ng of Nef/ml of medium. After 24 h, cells were assayed for apoptosis by TUNEL labeling, and then percent apoptosis was determined by fluorescent microscopic analysis of 10 fields per slide. Percent apoptosis was calculated as the number of FITC-labeled cells per total cell count. Data from two experiments performed in triplicate with 12 individually treated cell sets were pooled to generate average values and were used to determine standard errors (error bars). UT represents untreated cells. (B) PBMCs were either untreated or exposed to soluble Nef protein for 24 h. Apoptotic cells were detected by TUNEL, and then percent apoptosis in treated cells was compared to levels in untreated cells. Data from two experiments performed in triplicate with 12 individually treated cell sets were pooled to generate average values and were used to determine standard errors (error bars). (C and D) Representative images of Nef-treated PBMCs described for panel B. Images were taken via phase and fluorescence microscopy and arranged via Adobe Photoshop software (version 5.0.2; Adobe Systems). (C) Matched-phase image for panel D, which is the combined fluorescent images for TUNEL (FITC, green) and CD4 staining (Texas Red). Cells fluorescing yellow were simultaneously stained for TUNEL and CD4. Magnification, ×240.