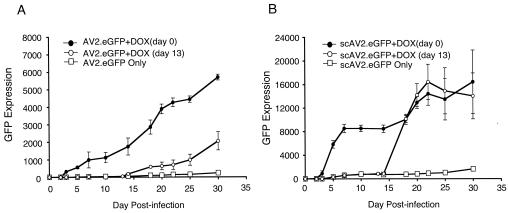
FIG. 6.
Doxorubicin induces rAAV transduction without directly enhancing the efficiency of second-strand synthesis. Polarized human airway epithelia grown at the air-liquid interface were infected with 5 × 109 particles of full-length AV2.eGFP (A) or self-complementary scAV2.eGFP (B) from the apical surface at day 0. GFP expression was quantified at the time points indicated on the graphs by fluorescent microscopy and the following calculation: the mean area of GFP fluorescence multiplied by the mean intensity of fluorescence. Ten images were acquired randomly from each experimental point. The following experimental protocols were performed: (i) rAAV infection without doxorubicin (DOX), (ii) rAAV infection in the presence of 5 μM doxorubicin, and (iii) rAAV infection without doxorubicin and subsequent application of 5 μM doxorubicin for 24 h at 13 days postinfection. Results depict the means ± standard errors of the means for three independent epithelia for each experimental point.