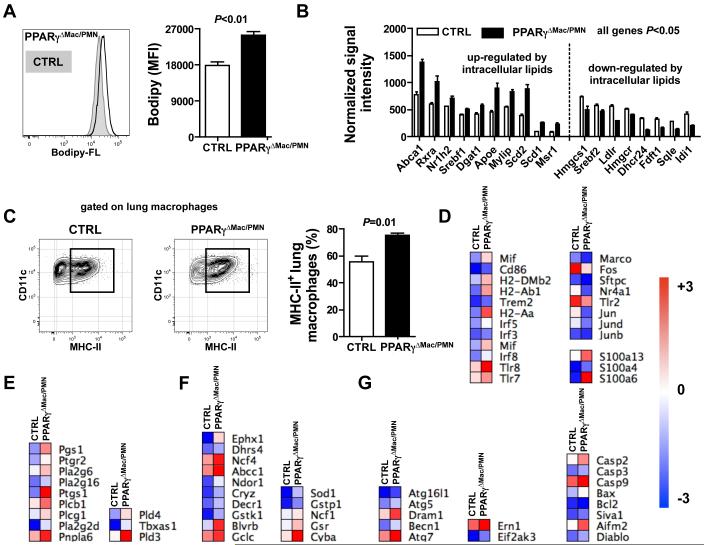
Figure 5. PPARγ is critical to preserve lung macrophage cellular homeostasis.
(A) Cellular lipid levels were assessed in resting lung macrophages from LysM-Cre × PPARγflox/flox mice (PPARγΔMac/PMN) and controls (CTRL) using Bofipy-FL staining (n=3 mice per group). (B) mRNA expression of genes modulated by intracellular lipid levels was determined by microarray. (C) Flow cytometry plot and quantification of cell surface MHC-II protein levels in lung macrophages from LysM-Cre × PPARγflox/flox mice (PPARγΔMac/PMN) and controls (CTRL) (n=3-4 mice per group). Heat maps representing mRNA levels of genes involved in macrophage activation (D), lipid signaling (E), oxidative stress signaling (F) and cell death/autophagy (G).